Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (8): 1415-1428.doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-024-3129-8
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Haoxiang YANG, Houbo SUN, Jinghao SHEN, Hao WU, Hongyuan JIANG*(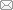 )
)
Received:2024-03-27
Online:2024-08-03
Published:2024-07-31
Contact:
Hongyuan JIANG
E-mail:jianghy@ustc.edu.cn
Supported by:2010 MSC Number:
Haoxiang YANG, Houbo SUN, Jinghao SHEN, Hao WU, Hongyuan JIANG. Dynamics of perinuclear actin ring regulating nuclear morphology. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(8): 1415-1428.
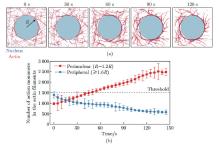
Fig. 3
Simulation results of perinuclear actin ring assembly:(a) the simulations showing that the perinuclear actin ring was formed after external stimuli; (b) the evolution of the actin distribution, i.e., the numbers of actin monomers in the actin filaments, in the perinuclear (red) and peripheral (blue) regions after external stimuli in simulation, where R is the radius of the nucleus. The black dashed line represents the threshold for perinuclear actin ring assembly. All error bars are standard deviations (color online)"
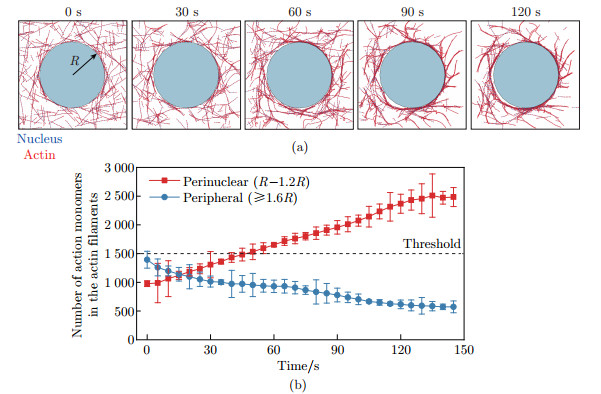
Fig. 4
The polymerization rate and the branching reaction of actin filaments can regulate perinuclear actin ring assembly. (a) The actin dynamics when vpoly=0.05 μ m/s; (b) and (c) the numbers of actin monomers in the (b) perinuclear and (c) peripheral actin filaments with different vpoly after external stimuli; (d) the actin dynamics when the the branching reaction is inhibited; (e) and (f) the numbers of actin monomers in the (e) perinuclear and (f) peripheral actin filaments with or without the branching reaction after external stimuli in simulation, where the black dashed line represents the threshold for perinuclear actin ring assembly (color online)"
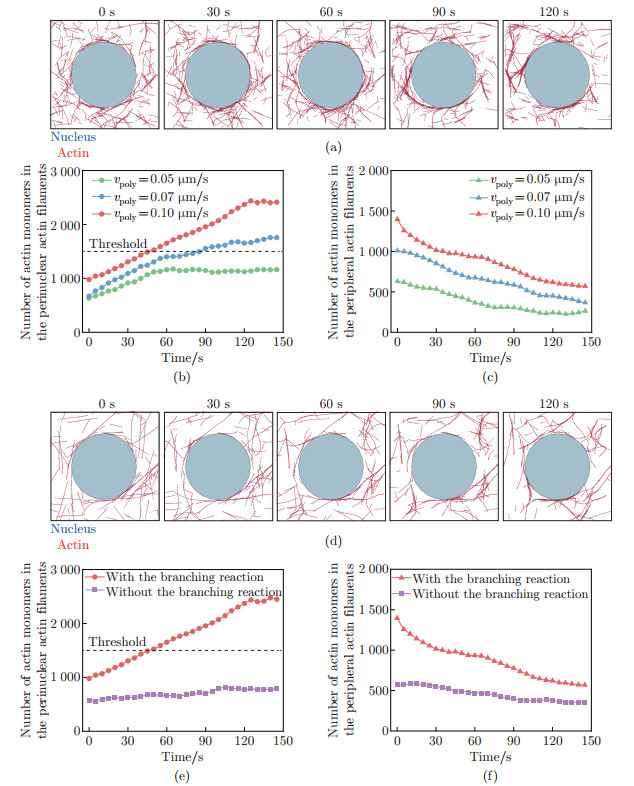
Fig. 5
Myosin II is another crucial factor that regulates perinuclear actin ring assembly. (a) and (b) The numbers of actin monomers in the (a) perinuclear and (b) peripheral actin filaments with different kbinding after external stimuli; (c) and (d) the numbers of actin monomers in the (c) perinuclear and (d) peripheral actin filaments with different kunbinding, 0 after external stimuli, where the black dashed line represents the threshold for perinuclear actin ring assembly (color online)"
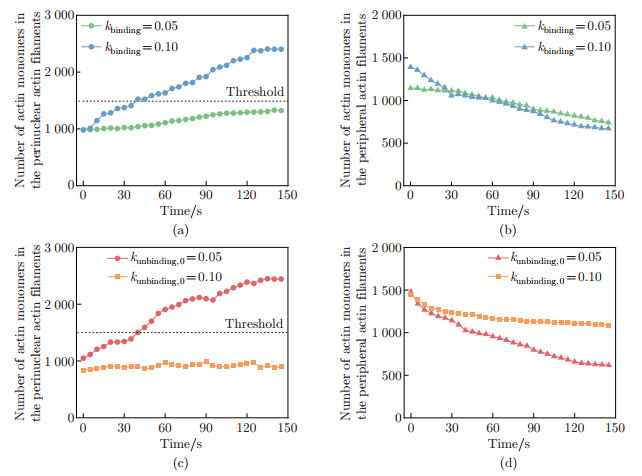
Fig. 6
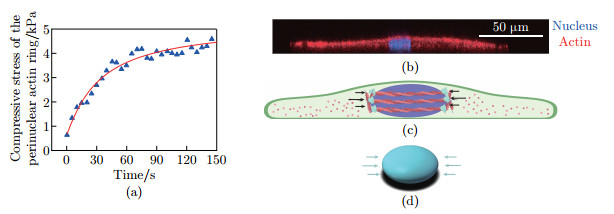
Finite element model of the nucleus subject to the compressive stress: (a) the time evolution of the compressive stress exerted by the perinuclear actin ring, where the blue triangles in the figure represent the data points simulated in the dynamics model, and the red curve is the fitted curve; (b) the fluorescence image of nucleus (blue) and actin (red) in side view of MDCK cells; (c) the schematic illustration of the perinuclear actin ring contraction; (d) the schematic illustration of finite element model (color online)"
| 1 | LECUIT,T.,LENNE,P. F., andMUNRO,E.Force generation, transmission, and integration during cell and tissue morphogenesis.Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology,27,157-184(2011) |
| 2 | STANKEVICINS,L.,ECKER,N.,TERRIAC,E.,MAIURI,P.,SCHOPPMEYER,R.,VARGAS,P.,LENNON-DUMENIL,A. M.,PIEL,M.,QU,B.,HOTH,M.,KRUSE,K., andLAUTENSCHLAGER,F.Deterministic actin waves as generators of cell polarization cues.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,117(2),826-835(2020) |
| 3 | SCHAKS,M.,GIANNONE,G., andROTTNER,K.Actin dynamics in cell migration.Essays in Biochemistry,63(5),483-495(2019) |
| 4 | BALDAUF,L.,VAN BUREN,L.,FANALISTA,F., andKOENDERINK,G. H.Actomyosin-driven division of a synthetic cell.ACS Synthetic Biology,11(10),3120-3133(2022) |
| 5 | MONDAL,C.,DI MARTINO,J. S., andBRAVO-CORDERO,J. J.Actin dynamics during tumor cell dissemination.International Review of Cell and Molecular Biology,360,65-98(2021) |
| 6 | GUNASEKARAN,S.,MIYAGAWA,Y., andMIYAMOTO,K.Actin nucleoskeleton in embryonic development and cellular differentiation.Current Opinion in Cell Biology,76,102100(2022) |
| 7 | HOYLE,N. P.,SEINKMANE,E.,PUTKER,M.,FEENEY,K. A.,KROGAGER,T. P.,CHESHAM,J. E.,BRAY,L. K.,THOMAS,J. M.,DUNN,K.,BLAIKLEY,J., andONEILL,J. S.Circadian actin dynamics drive rhythmic fibroblast mobilization during wound healing.Science Translational Medicine,9(415),eaal2774(2017) |
| 8 | MARTIN,P., andLEWIS,J.Actin cables and epidermal movement in embryonic wound healing.nature,360(6400) |
| 9 | OLSON,E. N., andNORDHEIM,A.Linking actin dynamics and gene transcription to drive cellular motile functions.Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology,11(5),353-365(2010) |
| 10 | JAFFE,A. B., andHALL,A.Rho GTPases: biochemistry and biology.Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology,21,247-269(2005) |
| 11 | VARTIAINEN,M. K.,GUETTLER,S.,LARIJANI,B., andTREISMAN,R.Nuclear actin regulates dynamic subcellular localization and activity of the SRF cofactor MAL.Science,316(5832),1749-1752(2007) |
| 12 | POSERN,G., andTREISMAN,R.Actin' together: serum response factor, its cofactors and the link to signal transduction.Trends in Cell Biology,16(11),588-596(2006) |
| 13 | LAPPALAINEN,P.,KOTILA,T.,JÉGOU,A., andROMET-LEMONNE,G.Biochemical and mechanical regulation of actin dynamics.Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology,23(12),836-852(2022) |
| 14 | ICHIKI,T.,WANG,T.,KENNEDY,A.,POOL,A. H.,EBISU,H.,ANDERSON,D. J., andOKA,Y.Sensory representation and detection mechanisms of gut osmolality change.nature,602(7897),468-474(2022) |
| 15 | CUI,Y.,HAMEED,F. M.,YANG,B.,LEE,K.,PAN,C. Q.,PARK,S., andSHEETZ,M.Cyclic stretching of soft substrates induces spreading and growth.Nature Communications,6(1),6333(2015) |
| 16 | NAVA,M. M.,MIROSHNIKOVA,Y. A.,BIGGS,L. C.,WHITEFIELD,D. B.,METGE,F.,BOUCAS,J.,VIHINEN,H.,JOKITALO,E.,LI,X.,GARCIA-ARCOS,J. M.,HOFFMANN,B.,MARKEL,R.,NIESSEN,C. M.,DAHL,K. N., andWICKSTRÖM,S. A.Heterochromatin-driven nuclear softening protects the genome against mechanical stress-induced damage.Cell,181(4),800-817(2020) |
| 17 | SHAO,X.,LI,Q.,MOGILNER,A.,BERSHADSKY,A. D., andSHIVASHANKAR,G. V.Mechanical stimulation induces formin-dependent assembly of a perinuclear actin rim.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,112(20),E2595-E2601(2015) |
| 18 | THIAM,H. R.,VARGAS,P.,CARPI,N.,CRESPO,C. L.,RAAB,M.,TERRIAC,E.,KING,M. C.,JACOBELLI,J.,ALBERTS,A. S.,STRADAL,T.,LENNON-DUMENIL,A., andPIEL,M.Perinuclear Arp2/3-driven actin polymerization enables nuclear deformation to facilitate cell migration through complex environments.Nature Communications,7(1),10997(2016) |
| 19 | RAHIMZADEH,J.,MENG,F.,SACHS,F.,WANG,J.,VERMA,D., andHUA,S. Z.Real-time observation of flow-induced cytoskeletal stress in living cells.American Journal of Physiology — Cell Physiology,301(3),C646-C652(2011) |
| 20 | WALES,P.,SCHUBERTH,C. E.,AUFSCHNAITER,R.,FELS,J.,GARCÍA-AGUILAR,I.,JANNING,A.,DLUGOS,C. P.,SCHÄFER-HERTE,M.,KLINGNER,C.,WÄLTE,M.,KUHLMANN,J.,MENIS,E.,HOCKADAY,KANG L.,MAIER,K. C.,HOU,W.,RUSSO,A.,HIGGS,H. N.,PAVENSTÄDT,H.,VOGL,T.,ROTH,J.,QUALMANN,B.,KESSELS,M. M.,MARTIN,D. E.,MULDER,B., andWEDLICH-SÖLDNER,R.Calcium-mediated actin reset (CaAR) mediates acute cell adaptations.eLife,5,e19850(2016) |
| 21 | FREEDMAN,S. L.,BANERJEE,S.,HOCKY,G. M., andDINNER,A. R.A versatile framework for simulating the dynamic mechanical structure of cytoskeletal networks.Biophysical Journal,113(2),448-460(2017) |
| 22 | HEAD,D. A.,LEVINE,A. J., andMACKINTOSH,F. C.Distinct regimes of elastic response and deformation modes of cross-linked cytoskeletal and semiflexible polymer networks.Physical Review E,68(6),061907(2003) |
| 23 | MACKINTOSH,F. C.,KAS,J., andJANMEY,P. A.Elasticity of semiflexible biopolymer networks.Physical Review Letters,75(24),4425-4428(1995) |
| 24 | ALBERTS,J. B.Biophysically realistic filament bending dynamics in agent-based biological simulation.PLoS One,4(3),e4748(2009) |
| 25 | BIDONE,T. C.,TANG,H., andVAVYLONIS,D.Dynamic network morphology and tension buildup in a 3D model of cytokinetic ring assembly.Biophysical Journal,107(11),2618-2628(2014) |
| 26 | NEDELEC,F., andFOETHKE,D.Collective Langevin dynamics of flexible cytoskeletal fibers.New Journal of Physics,9(11),427(2007) |
| 27 | RUBINSTEIN,M., andCOLBY,R. H.Polymer Physics,Oxford University Pres,New York(2003) |
| 28 | BROEDERSZ,C. P., andMACKINTOSH,F. C.Modeling semiflexible polymer networks.Reviews of Modern Physics,86(3),995-1036(2014) |
| 29 | SEPT,D.,ELCOCK,A. H., andMCCAMMON,J. A.Computer simulations of actin polymerization can explain the barbed-pointed end asymmetry.Journal of Molecular Biology,294(5),1181-1189(1999) |
| 30 | COFFMAN,V. C.,NILE,A. H.,LEE,I. J.,LIU,H., andWU,J. Q.Roles of formin nodes and myosin motor activity in Mid1p-dependent contractile-ring assembly during fission yeast cytokinesis.Molecular Biology of the Cell,20(24),5195-5210(2009) |
| 31 | VAVYLONIS,D.,WU,J. Q.,HAO,S.,O'SHAUGHNESSY,B., andPOLLARD,T. D.Assembly mechanism of the contractile ring for cytokinesis by fission yeast.Science,319(5859),97100(2008) |
| 32 | AROUSH,D. R. B.,OFER,N.,ABU-SHAH,E.,ALLARD,J.,KRICHEVSKY,O.,MOGILNER,A., andKEREN,K.Actin turnover in lamellipodial fragments.Current Biology,27(19),2963-2973(2017) |
| 33 | BRIEHER,W.Mechanisms of actin disassembly.Molecular Biology of the Cell,24(15),2299-2302(2013) |
| 34 | GRESSIN,L.,GUILLOTIN,A.,GUÉRIN,C.,BLANCHOIN,L., andMICHELOT,A.Architecture dependence of actin filament network disassembly.Current Biology,25(11),1437-1447(2015) |
| 35 | FUNK,J.,MERINO,F.,SCHAKS,M.,ROTTNER,K.,RAUNSER,S., andBIELING,P.A barbed end interference mechanism reveals how capping protein promotes nucleation in branched actin networks.Nature Communications,12(1),5329(2021) |
| 36 | SCHAFER,D. A.,JENNINGS,P. B., andCOOPER,J. A.Dynamics of capping protein and actin assembly in vitro: uncapping barbed ends by polyphosphoinositides.Journal of Cell Biology,135(1),169-179(1996) |
| 37 | HSIAO,J. Y.,GOINS,L. M.,PETEK,N. A., andMULLINS,R. D.Arp2/3 complex and cofilin modulate binding of tropomyosin to branched actin networks.Current Biology,25(12),1573-1582(2015) |
| 38 | SMITH,D. B., andLIU,J.Branching and capping determine the force-velocity relationships of branching actin networks.Physical Biology,10(1),016004(2013) |
| 39 | WEICHSEL,J., andSCHWARZ,U. S.Two competing orientation patterns explain experimentally observed anomalies in growing actin networks.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,107(14),6304-6309(2010) |
| 40 | GONG,B.,WEI,X.,QIAN,J., andLIN,Y.Modeling and simulations of the dynamic behaviors of actin-based cytoskeletal networks.ACS Biomaterials Science and Engineering,5(8),3720-3734(2019) |
| 41 | GONG,B.,LIN,J.,WEI,X.,QIAN,J., andLIN,Y.Cross-linked biopolymer networks with active motors: mechanical response and intra-network transport.Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids,127,80-93(2019) |
| 42 | GONG,B.,LIN,J., andQIAN,J.Growing actin networks regulated by obstacle size and shape.Acta Mechanica Sinica,33,222-233(2017) |
| 43 | POPOV,K.,KOMIANOS,J., andPAPOIAN,G. A.MEDYAN: mechanochemical simulations of contraction and polarity alignment in actomyosin networks.PLoS Computational Biology,12(4),e1004877(2016) |
| 44 | FERRER,J. M.,LEE,H.,CHEN,J.,PELZ,B.,NAKAMURA,F.,KAMM,R. D., andLANG,M. J.Measuring molecular rupture forces between single actin filaments and actin-binding proteins.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,105(27),9221-9226(2008) |
| 45 | PASQUALI,M.,SHANKAR,V., andMORSE,D. C.Viscoelasticity of dilute solutions of semiflexible polymers.Physical Review E,64(2),020802(2001) |
| 46 | STAM,S.,ALBERTS,J.,GARDEL,M. L., andMUNRO,E.Isoforms confer characteristic force generation and mechanosensation by myosin II filaments.Biophysical Journal,108(8),1997-2006(2015) |
| 47 | LAPORTE,D.,OJKIC,N.,VAVYLONIS,D., andWU,J. Q.α-actinin and fimbrin cooperate with myosin II to organize actomyosin bundles during contractile-ring assembly.Molecular Biology of the Cell,23(16),3094-3110(2012) |
| 48 | FINER,J. T.,SIMMONS,R. M., andSPUDICH,J. A.Single myosin molecule mechanics: piconewton forces and nanometre steps.nature,368(6467),113-119(1994) |
| 49 | KRON,S. J., andSPUDICH,J. A.Fluorescent actin filaments move on myosin fixed to a glass surface.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,83(17),6272-6276(1986) |
| 50 | SKAU,C. T., andKOVAR,D. R.Fimbrin and tropomyosin competition regulates endocytosis and cytokinesis kinetics in fission yeast.Current Biology,20(16),1415-1422(2010) |
| 51 | WU,J. Q.,BAHLER,J., andPRINGLE,J. R.Roles of a fimbrin and an α-actinin-like protein in fission yeast cell polarization and cytokinesis.Molecular Biology of the Cell,12(4),1061-1077(2001) |
| 52 | HU,L., andPAPOIAN,G. A.Molecular transport modulates the adaptive response of branched actin networks to an external force.The Journal of Physical Chemistry B,117(42),13388-13396(2013) |
| 53 | KOJIMA,H.,ISHIJIMA,A., andYANAGIDA,T.Direct measurement of stiffness of single actin filaments with and without tropomyosin by in vitro nanomanipulation.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,91(26),12962-12966(1994) |
| 54 | OTT,A.,MAGNASCO,M.,SIMON,A., andLIBCHABER,A.Measurement of the persistence length of polymerized actin using fluorescence microscopy.Physical Review E,48(3),R1642(1993) |
| 55 | LOUGHLIN,R.,HEALD,R., andNÉDÉLEC,F.A computational model predicts Xenopus meiotic spindle organization.Journal of Cell Biology,191(7),1239-1249(2010) |
| 56 | VEIGEL,C.,MOLLOY,J. E.,SCHMITZ,S., andKENDRICK-JONES,J.Load-dependent kinetics of force production by smooth muscle myosin measured with optical tweezers.Nature Cell Biology,5(11),980-986(2003) |
| 57 | HU,L., andPAPOIAN,G. A.Mechano-chemical feedbacks regulate actin mesh growth in lamellipodial protrusions.Biophysical Journal,98(8),1375-1384(2010) |
| 58 | POLLARD,T. D.Rate constants for the reactions of ATP-and ADP-actin with the ends of actin filaments.Journal of Cell Biology,103(6),2747-2754(2010) |
| 59 | SKRUBER,K.,READ,T. A., andVITRIOL,E. A.Reconsidering an active role for G-actin in cytoskeletal regulation.Journal of Cell Science,131(1),jcs203760(2018) |
| 60 | LAMMERDING,J.Mechanics of the Nucleus,Wiley,New York783-807(2011) |
| 61 | KIM,J. K.,LOUHGHALAM,A.,LEE,G.,SCHAFER,B. W.,WIRTZ,D., andKIM,D. H.Nuclear lamin A/C harnesses the perinuclear apical actin cables to protect nuclear morphology.Nature Communications,8(1),2123(2017) |
| 62 | RAAB,M.,GENTILI,M.,DE BELLY,H.,THIAM,H. R.,VARGAS,P.,JIMENEZ,A. J.,LAUTENSCHLAEGER,F.,VOITURIEZ,R.,LENNON-DUMENIL,A.,MANEL,N., andPIEL,M.ESCRT III repairs nuclear envelope ruptures during cell migration to limit DNA damage and cell death.Science,352(6283),359-362(2016) |
| 63 | XIA,Y.,IVANOVSKA,I. L.,ZHU,K.,SMITH,L.,IRIANTO,J.,PFEIFER,C. R.,ALVEY,C. M.,JI,J.,LIU,D.,CHO,S.,BENNETT,R. R.,LIU,A. J.,GREENBERG,R. A., andDISCHER,D. E.Nuclear rupture at sites of high curvature compromises retention of DNA repair factors.Journal of Cell Biology,217(11),3796-3808(2018) |
| 64 | SONG,Y.,SOTO,J.,CHEN,B.,HOFFMAN,T.,ZHAO,W.,ZHU,N.,PENG,Q.,LIU,L.,LY,C.,WONG,P., andLI,S.Transient nuclear deformation primes epigenetic state and promotes cell reprogramming.Nature Materials,21(10),1191-1199(2022) |
| 65 | WANG,Y.,SHIBASAKI,F., andMIZUNO,K.Calcium signal-induced cofilin dephosphorylation is mediated by Slingshot via calcineurin.Journal of Biological Chemistry,280(13),12683-12689(2005) |
| 66 | HEIDINGS,J. B.,DEMOSTHENE,B.,MERLINO,T. R.,CASTANEDA,N., andKANG,E. H.Gelsolin-mediated actin filament severing in crowded environments.Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,532(4),548-554(2020) |
| [1] | Huang Jing-chuan;Han Cheng-cai. INFLUENCES OF GAS NUCLEUS SCALE ON CAVITATION [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 1992, 13(4): 359-367. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||


 Email Alert
Email Alert RSS
RSS