Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (12): 2361-2384.doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-025-3320-7
Previous Articles Next Articles
Feng JIANG1,2, Lin DU1,3,4,†(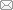 ), Qing XUE1,3,4, Zichen DENG1,2,3, C. GREBOGI5
), Qing XUE1,3,4, Zichen DENG1,2,3, C. GREBOGI5
Received:2025-05-07
Revised:2025-11-06
Published:2025-11-28
Contact:
Lin DU, E-mail: lindu@nwpu.edu.cnSupported by:2010 MSC Number:
Feng JIANG, Lin DU, Qing XUE, Zichen DENG, C. GREBOGI. Adaptive backward stepwise selection of fast sparse identification of nonlinear dynamics. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2025, 46(12): 2361-2384.
Algorithm 1
The key optimization procedure in the SINDy framework"
| 1: | procedure | |
| 2: | % input: | |
| 3: | % | |
| 4: | % | |
| 5: | % output: | |
| 6: | % | |
| 7: | | |
| 8: | for | |
| 9: | | |
| 10: | | |
| 11: | for | |
| 12: | | |
| 13: | | |
| 14: | end for | |
| 15: | end for | |
| 16: | end procedure |
Algorithm 2
The key optimization procedure in our ABSS-SINDy"
| 1: | procedure | |
| 2: | % input: | |
| 3: | % | |
| 4: | % | |
| 5: | % output: | |
| 6: | % | |
| 7: | % | |
| 8: | % | |
| 9: | | |
| 10: | for | |
| 11: | | |
| 12: | | |
| 13: | | |
| 14: | for | |
| 15: | | |
| 16: | | |
| 17: | | |
| 18: | | |
| 19: | calculate | |
| 20: | if the stopping criteria are not met | |
| 21: | then update | |
| 22: | end if | |
| 23: | end for | |
| 24: | | |
| 25: | end for | |
| 26: | end procedure |

Fig. 3
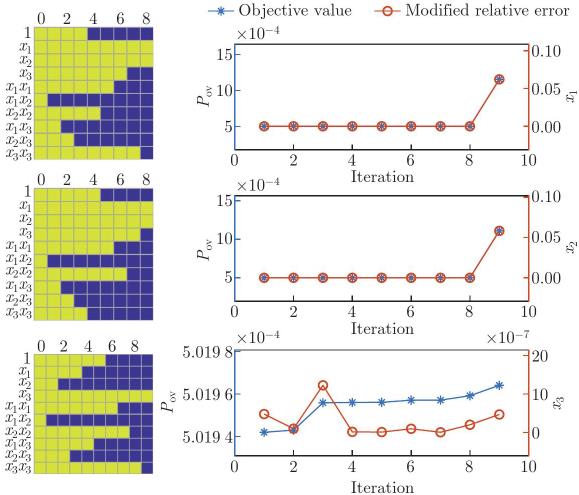
The process of the BSS. The left y-axis represents the object value (Pov), and the right y-axis represents the MRE. The hyperparameter kmax defined here will be accurately equal to the number of total features p minus the number of key feature [nkf]: (a) [kmax]1=8=p−[nkf]1; (b) [kmax]2=8=p−[nkf]2; (c) [kmax]3=9=p−[nkf]3 (color online)"
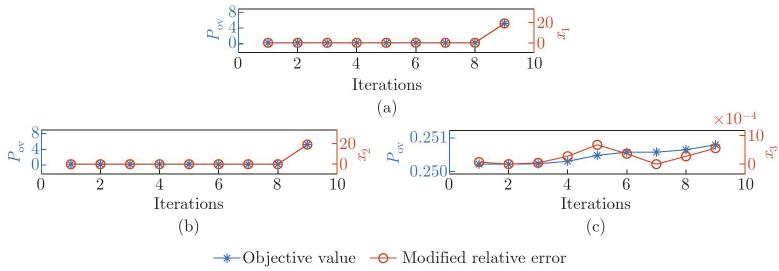

Fig. 4
The absolute value of coefficients on the same axis. (a) The red dots represent the initial estimated coefficients based on the LSE. The blue triangles represent the key features of the system. (b) The red circles represent the redundant features because the features will be deleted during the process of the BSS. The blue triangles represent the key features of the system (color online)"
Table 3
The initial solution based on the LSE (counterexample)"
| Structure | Coefficient | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.000 665 | |||
| 0.000 003 | |||
| 0.000 014 | |||
| 0.005 712 | 0.000 029 | ||
| 0.000 005 | 0.000 972 | ||
| 0.000 001 | 0.000 001 | ||
| 0.000 005 | 0.000 972 | ||
| 0.000 010 | 0.000 009 | ||
| 0.000 034 | |||
| 0.001 117 | |||
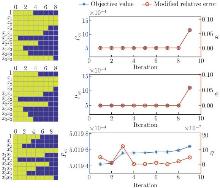
Fig. 9
The changes of the coefficients with the iteration. The yellow squares represent the non-zero coefficients, and the blue squares represent the zero coefficients. With BSS, the redundant features are deleted one by one, and the process will only end once the stopping criterion is reached (color online)"
| [1] | HASTIE, T., TIBSHIRANI, R., and WAINWRIGHT, M. Statistical Learning with Sparsity: the Lasso and Generalizations, CRC Press, Boca Raton (2015) |
| [2] | CANDES, E. J., ROMBERG, J., and TAO, T. Robust uncertainty principles: exact signal reconstruction from highly incomplete frequency information. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 52(2), 489–509 (2006) |
| [3] | DONOHO, D. L. Compressed sensing. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 52(4), 1289–1306 (2006) |
| [4] | WANG, W. X., YANG, R., LAI, Y. C., KOVANIS, V., and GREBOGI, C. Predicting catastrophes in nonlinear dynamical systems by compressive sensing. Physical Review Letters, 106(15), 154101 (2011) |
| [5] | WANG, W. X., LAI, Y. C., GREBOGI, C., and YE, J. P. Network reconstruction based on evolutionary-game data via compressive sensing. Physical Review X, 1(2), 021021 (2011) |
| [6] | WANG, W. X., YANG, R., LAI, Y. C., KOVANIS, V., and HARRISON, M. A. F. Time-series-based prediction of complex oscillator networks via compressive sensing. Europhysics Letters, 94(4), 48006 (2011) |
| [7] | WANG, W. X., LAI, Y. C., and GREBOGI, C. Data based identification and prediction of nonlinear and complex dynamical systems. Physics Reports, 644, 1–76 (2016) |
| [8] | LAI, Y. C. Finding nonlinear system equations and complex network structures from data: a sparse optimization approach. Chaos: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Nonlinear Science, 31(8), 082101 (2021) |
| [9] | CHEN, S. B. and DONOHO, D. Basis pursuit. Proceedings of 1994 28th Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, IEEE, Pacific Grove, 41–44 (1994) |
| [10] | TIBSHIRANI, R. Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series B: Statistical Methodological, 58(1), 267–288 (1996) |
| [11] | BRUNTON, S. L., PROCTOR, J. L., and KUTZ, J. N. Discovering governing equations from data by sparse identification of nonlinear dynamical systems. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 113(15), 3932–3937 (2016) |
| [12] | MANGAN, N. M., BRUNTON, S. L., PROCTOR, J. L., and KUTZ, J. N. Inferring biological networks by sparse identification of nonlinear dynamics. IEEE Transactions on Molecular, Biological and Multi-Scale Communications, 2(1), 52–63 (2016) |
| [13] | BRUNTON, S. L., PROCTOR, J. L., and KUTZ, J. N. Sparse identification of nonlinear dynamics with control (SINDYc). 10th IFAC Symposium on Nonlinear Control Systems, Monterey, 710–715 (2016) |
| [14] | KAISER, E., KUTZ, J. N., and BRUNTON, S. L. Sparse identification of nonlinear dynamics for model predictive control in the low-data limit. Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 474(2219), 20180335 (2018) |
| [15] | MANGAN, N. M., KUTZ, J. N., BRUNTON, S. L., and PROCTOR, J. L. Model selection for dynamical systems via sparse regression and information criteria. Proceedings of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 473(2204), 20170009 (2017) |
| [16] | RUDY, S. H., BRUNTON, S. L., PROCTOR, J. L., and KUTZ, J. N. Data-driven discovery of partial differential equations. Science Advances, 3(4), e1602614 (2017) |
| [17] | BONINSEGNA, L., NÜSKE, F., and CLEMENTI, C. Sparse learning of stochastic dynamical equations. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 148(24), 241723 (2018) |
| [18] | CHAMPION, K., LUSCH, B., KUTZ, J. N., and BRUNTON, S. L. Data-driven discovery of coordinates and governing equations. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United State of America, 116(45), 22445–22451 (2019) |
| [19] | CONTI, P., GOBAT, G., FRESCA, S., MANZONI, A., and FRANGI, A. Reduced order modeling of parametrized systems through autoencoders and SINDy approach: continuation of periodic solutions. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 411, 116072 (2023) |
| [20] | HIRSH, S. M., BARAJAS-SOLANO, D. A., and KUTZ, J. N. Sparsifying priors for Bayesian uncertainty quantification in model discovery. Royal Society Open Science, 9(2), 211823 (2022) |
| [21] | NAOZUKA, G. T., ROCHA, H. L., SILVA, R. S., and ALMEIDA, R. C. SINDy-SA framework: enhancing nonlinear system identification with sensitivity analysis. Nonlinear Dynamics, 110(3), 2589–2609 (2022) |
| [22] | SCHAEFFER, H. and MCCALLA, S. G. Sparse model selection via integral terms. Physical Review E, 96(2), 023302 (2017) |
| [23] | MESSENGER, D. A. and BORTZ, D. M. Weak SINDy: Galerkin-based data-driven model selection. Multiscale Modeling & Simulation, 19(3), 1474–1497 (2021) |
| [24] | WEI, B. L. Sparse dynamical system identification with simultaneous structural parameters and initial condition estimation. Chaos, Solitons and Fractals, 165, 112866 (2022) |
| [25] | LOISEAU, J. C. and BRUNTON, S. L. Constrained sparse Galerkin regression. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 838, 42–67 (2018) |
| [26] | LAI, Z. L. and NAGARAJAIAH, S. Sparse structural system identification method for nonlinear dynamic systems with hysteresis/inelastic behavior. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 117, 813–842 (2019) |
| [27] | LI, S. W., KAISER, E., LAIMA, S. J., LI, H., BRUNTON, S. L., and KUTZ, J. N. Discovering time-varying aerodynamics of a prototype bridge by sparse identification of nonlinear dynamical systems. Physical Review E, 100(2), 022220 (2019) |
| [28] | ZHANG, J. and MA, W. J. Data-driven discovery of governing equations for fluid dynamics based on molecular simulation. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 892, A5 (2020) |
| [29] | LIN, M. M., CHENG, C. M., PENG, Z. K., DONG, X. J., QU, Y. G., and MENG, G. Nonlinear dynamical system identification using the sparse regression and separable least-squares methods. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 505, 116141 (2021) |
| [30] | XIE, X. Y., SAMAEI, A., GUO, J. C., LIU, W. K., and GAN, Z. T. Data-driven discovery of dimensionless numbers and governing laws from scarce measurements. Nature Communications, 13(1), 7562 (2022) |
| [31] | BHADRIRAJU, B., NARASINGAM, A., and KWON, J. S. Machine learning-based adaptive model identification of systems: application to a chemical process. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 152, 372–383 (2019) |
| [32] | WANG, Z., HUAN, X., and GARIKIPATI, K. Variational system identification of the partial differential equations governing the physics of pattern-formation: inference under varying fidelity and noise. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 356, 44–74 (2019) |
| [33] | DE SILVA, B., CHAMPION, K., QUADE, M., LOISEAU, J. C., KUTZ, J., and BRUNTON, S. PySINDy: a Python package for the sparse identification of nonlinear dynamical systems from data. Journal of Open Source Software, 5(49), 2104 (2020) |
| [34] | KAPTANOGLU, A. A., DE SILVA, B. M., FASEL, U., KAHEMAN, K., GOLDSCHMIDT, A. J., CALLAHAM, J. L., DELAHUNT, C. B., NICOLAOU, Z. G., CHAMPION, K., LOISEAU, J. C., KUTZ, J. N., and BRUNTON, S. L. PySINDy: a comprehensive Python package for robust sparse system identification. Journal of Open Source Software, 7(69), 3994 (2022) |
| [35] | EGAN, K., LI, W. Z., and CARVALHO, R. Automatically discovering ordinary differential equations from data with sparse regression. Communications Physics, 7(1), 20 (2024) |
| [36] | CORTIELLA, A., PARK, K. C., and DOOSTAN, A. Sparse identification of nonlinear dynamical systems via reweighted l1-regularized least-squares. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 376, 113620 (2021) |
| [37] | JAMES, G., WITTEN, D., HASTIE, T., and TIBSHIRANI, R. An Introduction to Statistical Learning, Springer, New York (2013) |
| [38] | JIANG, F., DU, L., YANG, F., and DENG, Z. C. Regularized least absolute deviation-based sparse identification of dynamical systems. Chaos: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Nonlinear Science, 33(1), 013103 (2023) |
| [39] | YIN, Q., CAI, J. T., GONG, X., and DING, Q. Local parameter identification with neural ordinary differential equations. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 43(12), 1887–1900 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-022-2926-9 |
| [40] | PILLONETTO, G., DINUZZO, F., CHEN, T. S., DE NICOLAO, G., and LJUNG, L. Kernel methods in system identification, machine learning and function estimation: a survey. Automatica, 50(3), 657–682 (2014) |
| [41] | SCHAEFFER, H., TRAN, G., and WARD, R. Learning dynamical systems and bifurcation via group sparsity. arXiv Preprint, arXiv.1709.01558 (2017) |
| [42] | CHENG, C. M. and BAI, E. W. Variable selection based on squared derivative averages. Automatica, 127, 109491 (2021) |
| [43] | CAMPS-VALLS, G., GERHARDUS, A., NINAD, U., VARANDO, G., MARTIUS, G., BALAGUER-BALLESTER, E., VINUESA, R., DIAZ, E., ZANNA, L., and RUNGE, J. Discovering causal relations and equations from data. Physics Reports, 1044, 1–68 (2023) |
| [44] | KARNIADAKIS, G. E., KEVREKIDIS, I. G., LU, L., PERDIKARIS, P., WANG, S. F., and YANG, L. Physics-informed machine learning. Nature Reviews Physics, 3(6), 422–440 (2021) |
| [1] | Jun HU, Shudao ZHANG. Global sensitivity analysis based on high-dimensional sparse surrogate construction [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2017, 38(6): 797-814. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||


 Email Alert
Email Alert RSS
RSS