Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (11): 1875-1894.doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-024-3186-9
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Jinhui LIU1, Yu XUE1,2, Zhihong GAO1, A. O. KRUSHYNSKA2, Jinqiang LI1,*( )
)
Received:2024-06-25
Online:2024-11-03
Published:2024-10-30
Contact:
Jinqiang LI
E-mail:lijinqiang@hrbeu.edu.cn
Supported by:2010 MSC Number:
Jinhui LIU, Yu XUE, Zhihong GAO, A. O. KRUSHYNSKA, Jinqiang LI. Actively tunable sandwich acoustic metamaterials with magnetorheological elastomers. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(11): 1875-1894.
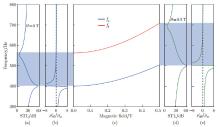
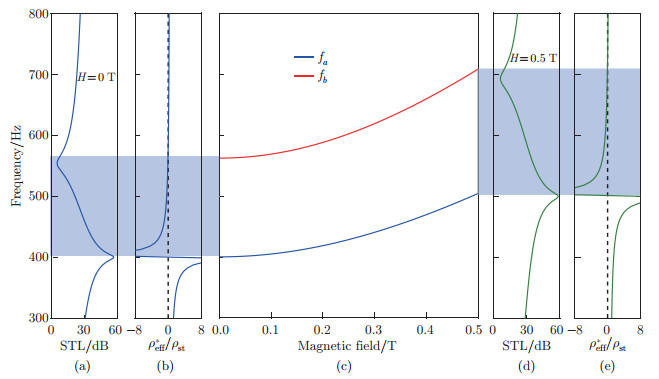
Fig. 9
(a) The STL and (b) the normalized effective dynamic mass density ρeff*/ρst at H=0 T, (c) effects of the magnetic field H on the sound insulation peak fa and the sound insulation valley fb, and (d) the STL and (e) the normalized effective dynamic mass density ρeff*/ρst at H=0.5 T of the MSP (color online)"
| 1 | SILVA,B. G.,ALVES,F.,SARDINHA,M.,REIS,L.,LEITE,M.,DEUS,A. M., andVAZ,M. F.Functionally graded cellular cores of sandwich panels fabricated by additive manufacturing.Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers Part L-Journal of Materials-Design and Applications,236(9),1814-1828(2022) |
| 2 | SUN,Y.,GUO,L. C.,WANG,T. S.,YAO,L. J., andSUN,X. Y.Bending strength and failure of single-layer and double-layer sandwich structure with graded truss core.Composite Structures,226,111204(2019) |
| 3 | MA,N. F.,HAN,Q.,HAN,S. H., andLI,C. L.Hierarchical re-entrant honeycomb metamaterial for energy absorption and vibration insulation.International Journal of Mechanical Sciences,250,108307(2023) |
| 4 | JIANG,T. J.,HAN,S. H.,HAN,Q., andLI,C. L.Design and optimization of the dual-functional lattice-origami metamaterials.Composite Structures,327,117670(2024) |
| 5 | FU,T.,CHEN,Z. B.,YU,H. Y.,WANG,Z. L., andLIU,X. X.An analytical study of sound transmission through stiffened double laminated composite sandwich plates.Aerospace Science and Technology,82-83,92-104(2018) |
| 6 | SHEN,C.,XIN,F. X., andLU,T. J.Sound transmission across composite laminate sandwiches: influence of orthogonal stiffeners and laminate layup.Composite Structures,143,310-316(2016) |
| 7 | WANG,D. W., andMA,L.Sound transmission through composite sandwich plate with pyramidal truss cores.Composite Structures,164,104-117(2017) |
| 8 | WANG,D. W.,MA,L., andWEN,Z. H.Sound transmission through a sandwich structure with two-layered pyramidal core and cavity absorption.Journal of Sound and Vibration,459,114853(2019) |
| 9 | LI,Y. L.,ZHANG,Y. L., andXIE,S. C.A lightweight multilayer honeycomb membrane-type acoustic metamaterial.Applied Acoustics,168,107427(2020) |
| 10 | OLIAZADEH,P.,FARSHIDIANFAR,A., andCROCKER,M. J.Experimental study and analytical modeling of sound transmission through honeycomb sandwich panels using SEA method.Composite Structures,280,114927(2022) |
| 11 | LI,Y. L.,YAN,J. H., andZHANG,Y. L.Low-frequency sound insulation of honeycomb membrane-type acoustic metamaterials with different interlayer characteristics.Journal of Vibration and Control,30(7-8),1422-1437(2024) |
| 12 | DE MELO,N.,CLAEYS,C.,DECKERS,E., andDESMET,W.Metamaterial foam core sandwich panel designed to attenuate the mass-spring-mass resonance sound transmission loss dip.Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing,139,106624(2020) |
| 13 | ZHOU,R., andCROCKER,M. J.Sound transmission loss of foam-filled honeycomb sandwich panels using statistical energy analysis and theoretical and measured dynamic properties.Journal of Sound and Vibration,329(6),673-686(2010) |
| 14 | ZHANG,Y. W.,SHE,G. L., andDING,H. X.Nonlinear resonance of graphene platelets reinforced metal foams plates under axial motion with geometric imperfections.European Journal of Mechanics A-Solids,98,104887(2023) |
| 15 | XIAO,Y.,WEN,J. H., andWEN,X. S.Sound transmission loss of metamaterial-based thin plates with multiple subwavelength arrays of attached resonators.Journal of Sound and Vibration,331(25),5408-5423(2012) |
| 16 | MEAD,D. J., andPUJARA,K. K.Space-harmonic analysis of periodically supported beams: response to convected random loading.Journal of Sound and Vibration,14(4),525-541(1971) |
| 17 | LEE,J. H., andKIM,J.Analysis of sound transmission through periodically stiffened panels by space-harmonic expansion method.Journal of Sound and Vibration,251(2),349-366(2002) |
| 18 | LEE,J. H., andKIM,J.Sound transmission through periodically stiffened cylindrical shells.Journal of Sound and Vibration,251(3),431-456(2002) |
| 19 | XIN,F. X., andLU,T. J.Analytical modeling of fluid loaded orthogonally rib-stiffened sandwich structures: sound transmission.Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids,58(9),1374-1396(2010) |
| 20 | WANG,M. F.,YI,K. J., andZHU,R.Tunable underwater low-frequency sound absorption via locally resonant piezoelectric metamaterials.Journal of Sound and Vibration,548,117514(2023) |
| 21 | YU,C. L.,DUAN,M. Y.,HE,W.,CHEN,X.,XIN,F. X., andLU,T. J.Grating-like anechoic layer for broadband underwater sound absorption.International Journal of Mechanical System Dynamics,2(3),265-277(2022) |
| 22 | MENG,H.,GALLAND,M. A.,ICHCHOU,M.,XIN,F. X., andLU,T. J.On the low frequency acoustic properties of novel multifunctional honeycomb sandwich panels with micro-perforated faceplates.Applied Acoustics,152,31-40(2019) |
| 23 | TANG,Y. F.,XIN,F. X., andLU,T. J.Sound absorption of micro-perforated sandwich panel with honeycomb-corrugation hybrid core at high temperatures.Composite Structures,226,111285(2019) |
| 24 | WANG,D. W.,MA,L.,WANG,X. T., andQI,G.Sound transmission loss of sandwich plate with pyramidal truss cores.Journal of Sandwich Structures & Materials,22(3),551-571(2020) |
| 25 | WANG,D. W.,MA,L.,WANG,X. T.,WEN,Z. H., andGLORIEUX,C.Sound transmission loss of laminated composite sandwich structures with pyramidal truss cores.Composite Structures,220,19-30(2019) |
| 26 | FU,T.,CHEN,Z. B.,YU,H. Y.,ZHU,X. Z., andZHAO,Y. Z.Sound transmission loss behavior of sandwich panel with different truss cores under external mean airflow.Aerospace Science and Technology,86,714-723(2019) |
| 27 | WANG,S.,ZHANG,X. C.,LI,F. M., andHOSSEINI,S. M.Sound transmission loss of a novel acoustic metamaterial sandwich panel: theory and experiment.Applied Acoustics,199,109035(2022) |
| 28 | XUE,Y.,LI,J. Q.,WANG,Y., andLI,F. M.Broadband vibration attenuation in nonlinear meta-structures with magnet coupling mechanism: theory and experiments.Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation,127,107543(2023) |
| 29 | WU,Z. J.,LIU,W. Y.,LI,F. M., andZHANG,C. Z.Band-gap property of a novel elastic metamaterial beam with X-shaped local resonators.Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing,134,106357(2019) |
| 30 | LIN,Q. H.,LIN,Q. L.,WANG,Y. H., andDI,G. Q.Sound insulation performance of sandwich structure compounded with a resonant acoustic metamaterial.Composite Structures,273,114312(2021) |
| 31 | WANG,Y. F.,WANG,Y. Z.,WU,B.,CHEN,W. Q., andWANG,Y. S.Tunable and active phononic crystals and metamaterials.Applied Mechanics Reviews,72,040801(2020) |
| 32 | GONG,X. T.,ZHOU,H. T.,ZHANG,S. C.,WANG,Y. F., andWANG,Y. S.Tunable sound transmission through water-air interface by membrane-sealed bubble metasurface.Applied Physics Letters,123,231703(2023) |
| 33 | GUO,W.,MA,Y. K.,WANG,Y. F.,LAUDE,V., andWANG,Y. S.Dual-tunable phononic waveguides for manipulation of guided Lamb waves.Programmable Materials,1,e11(2023) |
| 34 | CHANG,L. G.,LI,X. W.,GUO,Z. R.,CAO,Y. J.,LU,Y. Y.,GARZIEAR,R., andJIANG,H. Q.On-demand tunable metamaterials design for noise attenuation with machine learning.Materials & Design,238,112685(2024) |
| 35 | DENG,S. H.,HE,Y. Y.,WU,Y. D., andDING,W. P.A locally resonant metamaterial beam with tunable electromagnetic stiffness based on the electromechanical analogy network.Smart Materials and Structures,33(5),055052(2024) |
| 36 | YUAN,T. Y.,SONG,X.,XU,J. J.,PAN,B. R.,SUI,D.,XIAO,H. Y., andZHOU,J.Tunable acoustic composite metasurface based porous material for broadband sound absorption.Composite Structures,298,116014(2022) |
| 37 | ZHAO,T.,YANG,Z. C., andTIAN,W.Tunable nonlinear metastructure with periodic bi-linear oscillators for broadbend vibration suppression.Thin-Walled Structures,191,110975(2023) |
| 38 |
QUE,W. Z.,YANG,X. D., andZHANG,W.Tunable low frequency band gaps and sound transmission loss of a lever-type metamaterial plate.Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition),43(8),1145-1158(2022)
doi: 10.1007/s10483-022-2890-9 |
| 39 | YOON,D. S.,KIM,G. W., andCHOI,S. B.Response time of magnetorheological dampers to current inputs in a semi-active suspension system: modeling, control and sensitivity analysis.Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing,146,106999(2021) |
| 40 | HAN,W. J.,WANG,S.,RUI,X. T.,DONG,Y. Z., andCHOI,H. J.Core/shell magnetite/copolymer composite nanoparticles enabling highly stable magnetorheological response.International Journal of Mechanical System Dynamics,2(2),155-164(2022) |
| 41 | SETTET,A. T.,AGUIB,S.,NOUR,A., andZERROUNI,N.Study and analysis of the magneto-mechanical behavior of smart composite sandwich beam in elastomer.Mechanika,25(4),320-325(2019) |
| 42 | AGUIB,S.,NOUR,A.,BENKOUSSAS,B.,TAWFIQ,I.,DJEDID,T., andCHIKH,N.Numerical simulation of the nonlinear static behavior of composite sandwich beams with a magnetorheological elastomer core.Composite Structures,139,111-119(2016) |
| 43 | VEMULURI,R. B.,RAJAMOHAN,V., andARUMUGAM,A. B.Dynamic characterization of tapered laminated composite sandwich plates partially treated with magnetorheological elastomer.Journal of Sandwich Structures & Materials,20(3),308-350(2018) |
| 44 | LI,H.,WANG,W. Y.,WANG,Q. S.,HAN,Q. K.,LIU,J. G.,QIN,Z. Y.,XIONG,J., andWANG,X. P.Static and dynamic performances of sandwich plates with magnetorheological elastomer core: theoretical and experimental studies.Journal of Sandwich Structures & Materials,24(3),1556-1579(2022) |
| 45 | HOSEINZADEH,M., andREZAEEPAZHAND,J.Dynamic stability enhancement of laminated composite sandwich plates using smart elastomer layer.Journal of Sandwich Structures & Materials,22(8),2796-2817(2020) |
| 46 | WILLEY,C. L.,CHEN,V. W.,SCALZI,K. J.,BUSKOHL,P. R., andJUHL,A. T.A reconfigurable magnetorheological elastomer acoustic metamaterial.Applied Physics Letters,117,104102(2020) |
| 47 | HASHEMINEJAD,S. M., andSHABANIMOTLAGH,M.Magnetic-field-dependent sound transmission properties of magnetorheological elastomer-based adaptive panels.Smart Materials and Structures,19,035006(2010) |
| 48 | XUE,Y.,LI,J. Q.,WANG,Y.,SONG,Z. G., andKRUSHYNSKA,A. O.Widely tunable magnetorheological metamaterials with nonlinear amplification mechanism.International Journal of Mechanical Sciences,264,108830(2021) |
| 49 | LI,J. Q.,XUE,Y., andLI,F. M.Active band gap control of magnetorheological meta-plate using frequency feedback control law.Journal of Sound and Vibration,567,118076(2023) |
| 50 | WANG,Y. H.,YANG,J.,CHEN,Z. X.,GONG,X. L.,DU,H. P.,ZHANG,S. W.,LI,W. H., andSUN,S. S.Investigation of a novel MRE metamaterial sandwich beam with real-time tunable band gap characteristics.Journal of Sound and Vibration,527,116870(2022) |
| 51 | CHEN,Z. X.,SUN,S. S.,DENG,L.,YANG,J.,ZHANG,S. W.,DU,H. P., andLI,W. H.Investigation of a new metamaterial magnetorheological elastomer isolator with tunable vibration bandgaps.Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing,170,108806(2022) |
| 52 | WANG,L. Z.,CHEN,Z. B., andCHENG,L.A metamaterial plate with magnetorheological elastomers and gradient resonators for tuneable low-frequency and broadband flexural wave manipulation.Thin-Walled Structures,184,110521(2023) |
| 53 | WANG,Q.,CHEN,Z. X.,WANG,Y. H.,GONG,N.,YANG,J.,LI,W. H., andSUN,S. S.A metamaterial isolator with tunable low frequency stop-band based on magnetorheological elastomer and magnet spring.Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing,208,111029(2024) |
| 54 | LIN,Y.,YANG,J.,WANG,Y. H.,CHEN,Z. X.,GONG,L. P.,WANG,Q.,ZHANG,S. W.,LI,W. H., andSUN,S. S.Investigation of a new magnetorheological elastomer metamaterial plate with continuous programmable properties for vibration manipulation.Journal of Sound and Vibration,573,118215(2024) |
| 55 | LOU,C. C.,LIU,B.,CAO,X. F.,GAO,L.,XUAN,S. H.,DENG,H. X., andGONG,X. L.Dual-modulus 3D printing technology for magnetorheological metamaterials-part I: manufacturing and performance.Composites Part A-Applied Science and Manufacturing,176,107881(2024) |
| 56 | GORSHKOV,V. N.,BEREZNYKOV,O. V.,BOIGER,G. K.,SAREH,P., andFALLAH,A. S.Acoustic metamaterials with controllable bandgap gates based on magnetorheological elastomers.International Journal of Mechanical Sciences,238,107829(2023) |
| 57 | DAVIS,L. C.Model of magnetorheological elastomers.Journal of Applied Physics,85(6),3348-3351(1999) |
| 58 | XU,Z. L.,TONG,J., andWU,F. G.Magnetorheological elastomer vibration isolation of tunable three-dimensional locally resonant acoustic metamaterial.Solid State Communications,271,51-55(2018) |
| 59 | ZHANG,Y.,FAN,X. L.,LI,J. Q.,LI,F. M.,YU,G. C.,ZHANG,R. B., andYUAN,K. F.Low-frequency vibration insulation performance of the pyramidal lattice sandwich metamaterial beam.Composite Structures,278,114719(2021) |
| 60 | NARITA,Y.Layerwise optimization for the maximum fundamental frequency of laminated composite plates.Journal of Sound and Vibration,263(5),1005-1016(2003) |
| 61 | FAN,X. L.,LI,J. Q.,ZHANG,X. Y., andLI,F. M.Multi-bandgaps metamaterial plate design using complex mass-beam resonator.International Journal of Mechanical Sciences,236(15),107742(2022) |
| 62 | WANG,Q.,LI,J. Q., andLI,F. M.Bandgap properties in metamaterial sandwich plate with periodically embedded plate-type resonators.Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing,151,107375(2021) |
| 63 | LI,J. Q.,FAN,X. L., andLI,F. M.Numerical and experimental study of a sandwich-like metamaterial plate for vibration suppression.Composite Structures,238,111969(2020) |
| [1] | Honglin WAN, Xianghong LI, Yongjun SHEN. Study on vibration reduction of two-scale system coupled with dynamic vibration absorber [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(8): 1335-1352. |
| [2] | Chao WANG, Honggang ZHAO, Yang WANG, Jie ZHONG, Dianlong YU, Jihong WEN. Topology optimization of chiral metamaterials with application to underwater sound insulation [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(7): 1119-1138. |
| [3] | Meng LI, Hu DING. A vertical track nonlinear energy sink [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(6): 931-946. |
| [4] | Hongyan CHEN, Youcheng ZENG, Hu DING, Siukai LAI, Liqun CHEN. Dynamics and vibration reduction performance of asymmetric tristable nonlinear energy sink [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(3): 389-406. |
| [5] | Donghai HAN, Qi JIA, Yuanyu GAO, Qiduo JIN, Xin FANG, Jihong WEN, Dianlong YU. Local resonance metamaterial-based integrated design for suppressing longitudinal and transverse waves in fluid-conveying pipes [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(10): 1821-1840. |
| [6] | Jianing LIU, Jinqiang LI, Ying WU. Bandgap adjustment of a sandwich-like acoustic metamaterial plate with a frequency-displacement feedback control method [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(10): 1807-1820. |
| [7] | Peng SHENG, Xin FANG, Dianlong YU, Jihong WEN. Nonlinear metamaterial enabled aeroelastic vibration reduction of a supersonic cantilever wing plate [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(10): 1749-1772. |
| [8] | Jiawei MAO, Hao GAO, Junzhe ZHU, Penglin GAO, Yegao QU. Analytical modeling of piezoelectric meta-beams with unidirectional circuit for broadband vibration attenuation [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(10): 1665-1684. |
| [9] | Wenhao YUAN, Haitao LIAO, Ruxin GAO, Fenglian LI. Vibration and sound transmission loss characteristics of porous foam functionally graded sandwich panels in thermal environment [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2023, 44(6): 897-916. |
| [10] | Shengtao ZHANG, Jiaxi ZHOU, Hu DING, Kai WANG, Daolin XU. Fractional nonlinear energy sinks [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2023, 44(5): 711-726. |
| [11] | Xiangying GUO, Yunan ZHU, Zhong LUO, Dongxing CAO, Jihou YANG. Variable stiffness tuned particle dampers for vibration control of cantilever boring bars [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2023, 44(12): 2163-2186. |
| [12] | Wenzheng QUE, Xiaodong YANG, Wei ZHANG. Tunable low frequency band gaps and sound transmission loss of a lever-type metamaterial plate [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2022, 43(8): 1145-1158. |
| [13] | Hu DING, Yufei SHAO. NES cell [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2022, 43(12): 1793-1804. |
| [14] | Xiangying GUO, Yunan ZHU, Yegao QU, Dongxing CAO. Design and experiment of an adaptive dynamic vibration absorber with smart leaf springs [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2022, 43(10): 1485-1502. |
| [15] | Fengming LI;Zhiguang SONG. Vibration analysis and active control of nearly periodic two-span beams with piezoelectric actuator/sensor pairs [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2015, 36(3): 279-292. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||


 Email Alert
Email Alert RSS
RSS