Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (3): 389-406.doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-024-3095-9
• Articles • Next Articles
Hongyan CHEN1, Youcheng ZENG2, Hu DING2,*( ), Siukai LAI3, Liqun CHEN2
), Siukai LAI3, Liqun CHEN2
Received:2023-10-20
Online:2024-03-03
Published:2024-02-24
Contact:
Hu DING
E-mail:dinghu3@shu.edu.cn
Supported by:2010 MSC Number:
Hongyan CHEN, Youcheng ZENG, Hu DING, Siukai LAI, Liqun CHEN. Dynamics and vibration reduction performance of asymmetric tristable nonlinear energy sink. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(3): 389-406.
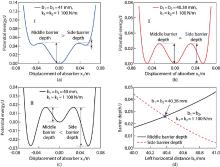
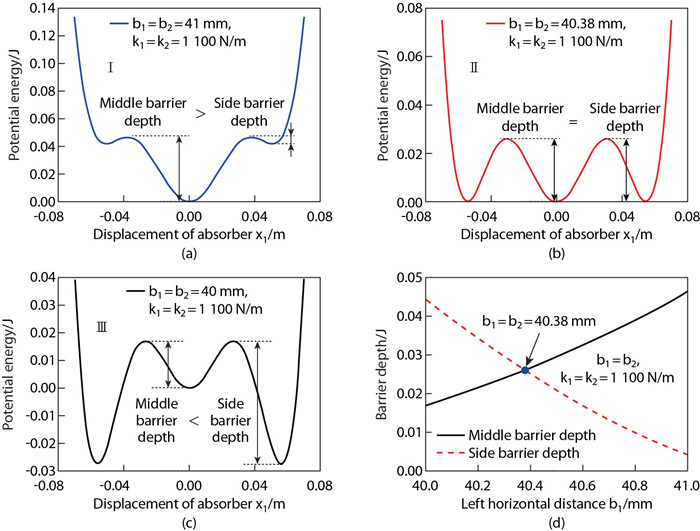
Fig. 5
(a) Ⅰ-TNES, where the middle barrier depth is greater than the side barrier depth; (b) Ⅱ-TNES, where the middle barrier depth is equal to the side barrier depth; (c) Ⅲ-TNES, where the middle barrier depth is less than the side barrier depth; (d) the potential barrier depth varies with the left horizontal distance b1 (color online)"
| 1 | VAKAKIS, A. F. Designing a linear structure with a local nonlinear attachment for enhanced energy pumping. Meccanica, 38 (6), 677- 686 (2003) |
| 2 | ZHANG, Y., KONG, X., YUE, C., and GUO, J. Characteristic analysis and design of nonlinear energy sink with cubic damping considering frequency detuning. Nonlinear Dynamics, 111 (17), 15817- 15836 (2023) |
| 3 | ZHANG, Y., KONG, X., and YUE, C. Experimental investigation of targeted energy transfers in strongly and nonlinearly coupled oscillators. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 116, 106837 (2023) |
| 4 | MCFARLAND, D. M., KERSCHEN, G., KOWTKO, J. J., LEE, Y. S., BERGMAN, L. A., and VAKAKIS, A. F. Experimental investigation of targeted energy transfers in strongly and nonlinearly coupled oscillators. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 118 (2), 791- 799 (2005) |
| 5 | RONCEN, T., MICHON, G., and MANET, V. Design and experimental analysis of a pneumatic nonlinear energy sink. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 190, 110088 (2023) |
| 6 | PHILIP, R., SANTHOSH, B., BALARAM, B., and AWREJCEWICZ, J. Vibration control in fluid conveying pipes using NES with nonlinear damping. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 194, 110250 (2023) |
| 7 | DEKEMELE, K., HABIB, G., and LOCCUFIER, M. The periodically extended stiffness nonlinear energy sink. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 169, 108706 (2022) |
| 8 | SAEED, A. S., ABDUL NASAR, R., and AL-SHUDEIFAT, M. A. A review on nonlinear energy sinks: designs, analysis and applications of impact and rotary types. Nonlinear Dynamics, 111 (1), 1- 37 (2022) |
| 9 | PHILIP, R., SANTHOSH, B., BALARAM, B., and AWREJCEWICZ, J. Vibration control in fluid conveying pipes using NES with nonlinear damping. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 194, 110250 (2023) |
| 10 | JI, J. C. Design of a nonlinear vibration absorber using three-to-one internal resonances. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 42 (1-2), 236- 246 (2014) |
| 11 | TANG, Y., WANG, G., YANG, T., and DING, Q. Nonlinear dynamics of three-directional functional graded pipes conveying fluid with the integration of piezoelectric attachment and nonlinear energy sink. Nonlinear Dynamics, 111 (3), 2415- 2442 (2022) |
| 12 |
WANG, X., MAO, X. Y., DING, H., LAI, S. K., and CHEN, L. Q. Multi-resonance inhibition of a two-degree-of-freedom piecewise system by one nonlinear energy sink. International Journal of Dynamics and Control, (2023)
doi: 10.1007/s40435-023-01337-9 |
| 13 |
LI, S. B., and DING, H. A cellular strategy for enhancing the adaptability of nonlinear energy sinks to strong excitation. International Journal of Dynamics and Control, (2023)
doi: 10.1007/s40435-023-01335-x |
| 14 | CAO, Y., YAO, H., LI, H., and DOU, J. Torsional vibration dynamics of a gear-shafting system attaching a nonlinear energy sink. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 176, 109172 (2022) |
| 15 | YAO, H., CAO, Y., DING, Z., and WEN, B. Using grounded nonlinear energy sinks to suppress lateral vibration in rotor systems. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 124, 237- 253 (2019) |
| 16 | DOU, J., YAO, H., LI, H., CAO, Y., and LIANG, S. Vibration suppression of multi-frequency excitation using cam-roller nonlinear energy sink. Nonlinear Dynamics, 111 (13), 11939- 11964 (2023) |
| 17 | YAO, H., CAO, Y., ZHANG, S., and WEN, B. A novel energy sink with piecewise linear stiffness. Nonlinear Dynamics, 94 (3), 2265- 2275 (2018) |
| 18 | KREMER, D., and LIU, K. A nonlinear energy sink with an energy harvester: transient responses. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 288, 116211 (2023) |
| 19 | WANG, J., WIERSCHEM, N., SPENCER, B. F., and LU, X. Experimental study of track nonlinear energy sinks for dynamic response reduction. Engineering Structures, 333 (20), 4859- 4880 (2014) |
| 20 | GENG, X. F., DING, H., MAO, X. Y., and CHEN, L. Q. A ground-limited nonlinear energy sink. Acta Mechanica Sinica, 38 (5), 521558 (2022) |
| 21 | GENG, X. F., and DING, H. Two-modal resonance control with an encapsulated nonlinear energy sink. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 520, 116667 (2022) |
| 22 | GENG, X., DING, H., MAO, X., and CHEN, L. Nonlinear energy sink with limited vibration amplitude. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 156, 107625 (2021) |
| 23 | BOROSON, E., MISSOUM, S., MATTEI, P. O., and VERGEZ, C. Optimization under uncertainty of parallel nonlinear energy sinks. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 394, 451- 464 (2017) |
| 24 |
DING, H., and SHAO, Y. NES cell. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 43 (12), 1793- 1804 (2022)
doi: 10.1007/s10483-022-2934-6 |
| 25 | ZANG, J., YUAN, T. C., LU, Z. Q., ZHANG, Y. W., DING, H., and CHEN, L. Q. A lever-type nonlinear energy sink. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 437, 119- 134 (2018) |
| 26 | CAO, Y., LI, Z., DOU, J., JIA, R., and YAO, H. An inerter nonlinear energy sink for torsional vibration suppression of the rotor system. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 537, 117184 (2022) |
| 27 | WANG, J., ZHANG, C., LI, H., and LIU, Z. Experimental and numerical studies of a novel track bistable nonlinear energy sink with improved energy robustness for structural response mitigation. Engineering Structures, 237, 112184 (2021) |
| 28 | ZUO, H., and ZHU, S. Bistable track nonlinear energy sinks with nonlinear viscous damping for impulsive and seismic control of frame structures. Engineering Structures, 272, 114982 (2022) |
| 29 | HUBBARD, S. A., MCFARLAND, D. M., BERGMAN, L. A., and VAKAKIS, A. F. Targeted energy transfer between a model flexible wing and nonlinear energy sink. Journal of Aircraft, 47 (6), 1918- 1931 (2010) |
| 30 | BERGEOT, B., BELLIZZI, S., and COCHELIN, B. Passive suppression of helicopter ground resonance using nonlinear energy sinks attached on the helicopter blades. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 392, 41- 55 (2017) |
| 31 | GOURC, E., SEGUY, S., MICHON, G., BERLIOZ, A., and MANN, B. P. Quenching chatter instability in turning process with a vibro-impact nonlinear energy sink. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 355, 392- 406 (2015) |
| 32 | GOURC, E., SEGUY, S., MICHON, G., and BERLIOZ, A. Chatter control in turning process with a nonlinear energy sink. Advanced Materials Research, 698, 89- 98 (2013) |
| 33 | FANG, S., ZHOU, S., YURCHENKO, D., YANG, T., and LIAO, W. H. Multistability phenomenon in signal processing, energy harvesting, composite structures, and metamaterials: a review. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 166, 108419 (2022) |
| 34 | ZOU, D., LIU, G., RAO, Z., TAN, T., ZHANG, W., and LIAO, W. H. Design of a multi-stable piezoelectric energy harvester with programmable equilibrium point configurations. Applied Energy, 302, 117585 (2021) |
| 35 | MEI, X., ZHOU, S., YANG, Z., KAIZUKA, T., and NAKANO, K. Enhancing energy harvesting in low-frequency rotational motion by a quad-stable energy harvester with time-varying potential wells. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 148, 107167 (2021) |
| 36 | ZOU, D., CHEN, K., RAO, Z., CAO, J., and LIAO, W. H. Design of a quad-stable piezoelectric energy harvester capable of programming the coordinates of equilibrium points. Nonlinear Dynamics, 108 (2), 857- 871 (2022) |
| 37 | ZHOU, S., LALLART, M., and ERTURK, A. Multistable vibration energy harvesters: principle, progress, and perspectives. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 528, 116886 (2022) |
| 38 | WANG, G., LIAO, W. H., ZHAO, Z., TAN, J., CUI, S., WU, H., and WANG, W. Nonlinear magnetic force and dynamic characteristics of a tri-stable piezoelectric energy harvester. Nonlinear Dynamics, 97 (4), 2371- 2397 (2019) |
| 39 | YAO, H., WANG, Y., CAO, Y., and WEN, B. Multi-stable nonlinear energy sink for rotor system. International Journal of Non-Linear Mechanics, 118, 103273 (2020) |
| 40 | YAO, H., WANG, Y., XIE, L., and WEN, B. Bi-stable buckled beam nonlinear energy sink applied to rotor system. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 138, 106546 (2020) |
| 41 | DOU, J., YAO, H., CAO, Y., HAN, S., and BAI, R. Enhancement of bistable nonlinear energy sink based on particle damper. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 547, 117547 (2023) |
| 42 | AL-SHUDEIFAT, M. A. Highly efficient nonlinear energy sink. Nonlinear Dynamics, 76 (4), 1905- 1920 (2014) |
| 43 | ROMEO, F., MANEVITCH, L. I., BERGMAN, L. A., and VAKAKIS, A. Transient and chaotic low-energy transfers in a system with bistable nonlinearity. Chaos, 25 (5), 053109 (2015) |
| 44 | DOU, J., LI, Z., CAO, Y., YAO, H., and BAI, R. Magnet based bi-stable nonlinear energy sink for torsional vibration suppression of rotor system. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 186, 109859 (2023) |
| 45 | REZAEI, M., and TALEBITOOTI, R. Investigating the performance of tri-stable magneto-piezoelastic absorber in simultaneous energy harvesting and vibration isolation. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 102, 661- 693 (2022) |
| 46 | REZAEI, M., TALEBITOOTI, R., and LIAO, W. H. Exploiting bi-stable magneto-piezoelastic absorber for simultaneous energy harvesting and vibration mitigation. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 207, 106618 (2021) |
| 47 | REZAEI, M., TALEBITOOTI, R., and LIAO, W. H. Investigations on magnetic bistable PZT-based absorber for concurrent energy harvesting and vibration mitigation: numerical and analytical approaches. Energy, 239, 122376 (2022) |
| 48 | YAO, H., CAO, Y., WANG, Y., and WEN, B. A tri-stable nonlinear energy sink with piecewise stiffness. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 463, 114971 (2019) |
| 49 | GIRI, A. M., ALI, S. F., and AROCKIARAJAN, A. Dynamics of symmetric and asymmetric potential well-based piezoelectric harvesters: a comprehensive review. Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, 32 (17), 1881- 1947 (2021) |
| 50 | WANG, G., ZHENG, Y., ZHU, Q., LIU, Z., and ZHOU, S. Asymmetric tristable energy harvester with a compressible and rotatable magnet-spring oscillating system for energy harvesting enhancement. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 543, 117384 (2023) |
| 51 | WANG, G., ZHAO, Z., LIAO, W. H., TAN, J., JU, Y., and LI, Y. Characteristics of a tri-stable piezoelectric vibration energy harvester by considering geometric nonlinearity and gravitation effects. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 138, 106571 (2020) |
| 52 | MEI, X., ZHOU, S., YANG, Z., KAIZUKA, T., and NAKANO, K. The benefits of an asymmetric tri-stable energy harvester in low-frequency rotational motion. Applied Physics Express, 12 (5), 057002 (2019) |
| 53 | LI, H. T., DING, H., JING, X. J., QIN, W. Y., and CHEN, L. Q. Improving the performance of a tri-stable energy harvester with a staircase-shaped potential well. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 159, 107805 (2021) |
| 54 | REZAEI, M., and TALEBITOOTI, R. Investigating the performance of tri-stable magneto-piezoelastic absorber in simultaneous energy harvesting and vibration isolation. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 102, 661- 693 (2022) |
| 55 | ZENG, Y. C., and DING, H. A tristable nonlinear energy sink. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 238, 107839 (2023) |
| 56 | ZENG, Y. C., DING, H., JI, J. C., JING, X. J., and CHEN, L. Q. A tristable nonlinear energy sink to suppress strong excitation vibration. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 202, 110694 (2023) |
| [1] | Honglin WAN, Xianghong LI, Yongjun SHEN. Study on vibration reduction of two-scale system coupled with dynamic vibration absorber [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(8): 1335-1352. |
| [2] | Meng LI, Hu DING. A vertical track nonlinear energy sink [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(6): 931-946. |
| [3] | Jianguo CUI, Tianzhi YANG, Wenju HAN, Liang LI, Muqing NIU, Liqun CHEN. Tunable topological interface states via a parametric system in composite lattices with/without symmetric elements [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(12): 2055-2074. |
| [4] | Jinxin DOU, Zhenping LI, Hongliang YAO, Muchuan DING, Guochong WEI. Torsional vibration suppression and electromechanical coupling characteristics of electric drive system considering misalignment [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(11): 1987-2010. |
| [5] | Jinhui LIU, Yu XUE, Zhihong GAO, A. O. KRUSHYNSKA, Jinqiang LI. Actively tunable sandwich acoustic metamaterials with magnetorheological elastomers [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(11): 1875-1894. |
| [6] | Jianing LIU, Jinqiang LI, Ying WU. Bandgap adjustment of a sandwich-like acoustic metamaterial plate with a frequency-displacement feedback control method [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(10): 1807-1820. |
| [7] | Jiawei MAO, Hao GAO, Junzhe ZHU, Penglin GAO, Yegao QU. Analytical modeling of piezoelectric meta-beams with unidirectional circuit for broadband vibration attenuation [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(10): 1665-1684. |
| [8] | Yong WANG, Peili WANG, Haodong MENG, Liqun CHEN. Dynamic performance and parameter optimization of a half-vehicle system coupled with an inerter-based X-structure nonlinear energy sink [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(1): 85-110. |
| [9] | Yang JIN, Tianzhi YANG. Enhanced vibration suppression and energy harvesting in fluid-conveying pipes [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2023, 44(9): 1487-1496. |
| [10] | Hu DING, J. C. JI. Vibration control of fluid-conveying pipes: a state-of-the-art review [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2023, 44(9): 1423-1456. |
| [11] | Shengtao ZHANG, Jiaxi ZHOU, Hu DING, Kai WANG, Daolin XU. Fractional nonlinear energy sinks [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2023, 44(5): 711-726. |
| [12] | Xiangying GUO, Yunan ZHU, Zhong LUO, Dongxing CAO, Jihou YANG. Variable stiffness tuned particle dampers for vibration control of cantilever boring bars [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2023, 44(12): 2163-2186. |
| [13] | Weixing ZHANG, Wei ZHANG, Xiangying GUO. Vertical vibration control using nonlinear energy sink with inertial amplifier [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2023, 44(10): 1721-1738. |
| [14] | A. MOSLEMI, M. R. HOMAEINEZHAD. Effects of viscoelasticity on the stability and bifurcations of nonlinear energy sinks [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2023, 44(1): 141-158. |
| [15] | Wanli YANG, Renzhong HONG, Yunbo WANG, Yuantai HU. Effects of mechanical loadings on the performance of a piezoelectric hetero-junction [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2022, 43(5): 615-626. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||


 Email Alert
Email Alert RSS
RSS