Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (11): 1987-2010.doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-024-3179-6
• Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Jinxin DOU1, Zhenping LI2, Hongliang YAO1,*( ), Muchuan DING1, Guochong WEI1
), Muchuan DING1, Guochong WEI1
Received:2024-04-19
Online:2024-11-03
Published:2024-10-30
Contact:
Hongliang YAO
E-mail:hlyao@mail.neu.edu.cn
Supported by:2010 MSC Number:
Jinxin DOU, Zhenping LI, Hongliang YAO, Muchuan DING, Guochong WEI. Torsional vibration suppression and electromechanical coupling characteristics of electric drive system considering misalignment. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(11): 1987-2010.
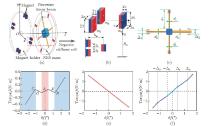
Fig. 5
Structural and schematic diagrams: (a) structure of the MNES, (b) schematic of piecewise linear stiffness, (c) schematic of negative stiffness, (d) force-displacement curve of the MNES, (e) force-displacement curve of the piecewise linear beams, and (f) force-displacement curve of the magnets (color online)"

| 1 | XU, K., WU, X., WANG, D. X., and LIU, X. Q. Electromechanical coupling modeling and motor current signature analysis of bolt loosening of industrial robot joint. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 184, 109681 (2023) |
| 2 | CHEN, X., WEI, H. B., DENG, T., HE, Z. Y., and ZHAO, S. E. Investigation of electromechanical coupling torsional vibration and stability in a high-speed permanent magnet synchronous motor driven system. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 64, 235- 248 (2018) |
| 3 | HUO, J. Z., WU, H. Y., SUN, W., ZHANG, Z. G., WANG, L. P., and DONG, J. H. Electromechanical coupling dynamics of TBM main drive system. Nonlinear Dynamics, 90 (4), 2687- 2710 (2017) |
| 4 | SZOLC, T., KONOWROCKI, R., MICHAJW, M., and PRȨGOWSKA, A. An investigation of the dynamic electromechanical coupling effects in machine drive systems driven by asynchronous motors. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 9, 118- 134 (2014) |
| 5 | YOUSFI, B. E., SOUALHI, A., MEDJAHER, K., and GUILLET, F. Electromechanical modeling of a motor-gearbox system for local gear tooth faults detection. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 166, 108435 (2022) |
| 6 | CHEN, S., and HU, M. H. Active torsional vibration suppression of hybrid electric vehicle drive system based on optimal harmonic current instruction calculation method. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 205, 110837 (2023) |
| 7 | HU, J. J., DENG, C. H., YANG, D. Z., YANG, Y., and JIA, M. X. Optimal energy consumption and torque fluctuation control of integrated electric drive system based on mechanical-electromagnetic-thermal coupling characteristics. Energy, 247, 123504 (2022) |
| 8 | GAO, P., WALKER, P. D., LIU, H., ZHOU, S. L., and XIANG, C. L. Application of an adaptive tuned vibration absorber on a dual lay-shaft dual clutch transmission powertrain for vibration reduction. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 121, 725- 744 (2019) |
| 9 | LIU, C. Z., YIN, X. S., LIAO, Y. H., YI, Y. Y., and QIN, D. T. Hybrid dynamic modeling and analysis of the electric vehicle planetary gear system. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 150, 103860 (2020) |
| 10 | LIANG, X. H., ZHANG, H. S., LIU, L. B., and ZUO, M. J. The influence of tooth pitting on the mesh stiffness of a pair of external spur gears. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 106, 1- 15 (2016) |
| 11 | CHE, X. Y., and ZHU, R. P. Nonlinear dynamic analysis of helical gear-rotor-bearing coupled system based on bearing load calculation with TRB clearance. Nonlinear Dynamics, 111 (19), 17787- 17807 (2023) |
| 12 | WEI, J., ZHANG, A. Q., WANG, G. Q., QIN, D. T., LIM, T. C., WANG, Y. W., and LIN, T. J. A study of nonlinear excitation modeling of helical gears with modification: theoretical analysis and experiments. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 128, 314- 335 (2018) |
| 13 | LIU, G. H., HONG, J., and PARKER, R. G. Influence of simultaneous time-varying bearing and tooth mesh stiffness fluctuations on spur gear pair vibration. Nonlinear Dynamics, 97 (2), 1403- 1424 (2019) |
| 14 | SONG, C. S., BAI, H., ZHU, C. C., WANG, Y. W., FENG, Z. H., and WANG, Y. Computational investigation of off-sized bearing rollers on dynamics for hypoid gear-shaft-bearing coupled system. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 156, 104177 (2021) |
| 15 | HAN, Q. K., and CHU, F. L. Dynamic behaviors of a geared rotor system under time-periodic base angular motions. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 78, 1- 14 (2014) |
| 16 | JIN, Y. L., LIU, Z. W., YANG, Y., LI, F. S., and CHEN, Y. S. Nonlinear vibrations of a dual-rotor-bearing-coupling misalignment system with blade-casing rubbing. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 97, 115948 (2021) |
| 17 | CHEN, S., and HU, M. H. Active torsional vibration suppression of integrated electric drive system based on optimal harmonic current instruction analytic calculation method. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 180, 105136 (2023) |
| 18 | HU, J. J., GUO, Q., SUN, Z. C., and YANG, D. Z. Study on low-frequency torsional vibration suppression of integrated electric drive system considering nonlinear factors. Energy, 284, 129251 (2023) |
| 19 | VAKAKIS, A. F., GENDELMAN, O. V., BERGMAN, L. A., MOJAHED, A., and GZAL, M. Nonlinear targeted energy transfer: state of the art and new perspectives. Nonlinear Dynamics, 108 (2), 711- 741 (2022) |
| 20 | GENDELMAN, O. V., and ALLONI, A. Forced system with vibro-impact energy sink: chaotic strongly modulated responses. Procedia IUTAM, 19, 53- 64 (2016) |
| 21 |
MOSLEMI, A., and HOMAEINEZHAD, M. R. Effects of viscoelasticity on the stability and bifurcations of nonlinear energy sinks. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 4 (1), 141- 158 (2023)
doi: 10.1007/s10483-023-2944-9 |
| 22 | DEKEMELE, K., and HABIB, G. Inverted resonance capture cascade: modal interactions of a nonlinear energy sink with softening stiffness. Nonlinear Dynamics, 111 (11), 9839- 9861 (2023) |
| 23 |
CHEN, H. Y., ZENG, Y. C., DING, H., LAI, S. K., and CHEN, L. Q. Dynamics and vibration reduction performance of asymmetric tristable nonlinear energy sink. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 5 (3), 389- 406 (2024)
doi: 10.1007/s10483-024-3095-9 |
| 24 |
LI, M., and DING, H. A vertical track nonlinear energy sink. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 5 (6), 931- 946 (2024)
doi: 10.1007/s10483-024-3127-6 |
| 25 | DOU, J. X., LI, Z. P., CAO, Y. B., YAO, H. L., and BAI, R. X. Magnet based bi-stable nonlinear energy sink for torsional vibration suppression of rotor system. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 186, 109859 (2023) |
| 26 | ZENG, Y. C., DING, H., JI, J. C., JING, X. J., and CHEN, L. Q. A tristable nonlinear energy sink to suppress strong excitation vibration. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 202, 110694 (2023) |
| 27 | XU, K. F., NIU, M. Q., ZHANG, Y. W., MENG, C. Y., and CHEN, L. Q. A nonlinear energy sink enhanced by active varying stiffness for spacecraft structure: theory, simulation, and experiment. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 204, 110787 (2023) |
| 28 |
ZHANG, S. T., ZHOU, J. X., DING, H., WANG, K., and XU, D. L. Fractional nonlinear energy sinks. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 4 (5), 711- 726 (2023)
doi: 10.1007/s10483-023-2984-9 |
| 29 | DOU, J. X., YAO, H. L., LI, H., GAO, D. Y., and HAN, S. D. Torsional vibration suppression of a spline-rotor system using a multi-stable nonlinear energy sink. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 211, 111240 (2024) |
| 30 | LI, S. B., ZHOU, X. X., and CHEN, J. E. Hamiltonian dynamics and targeted energy transfer of a grounded bistable nonlinear energy sink. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 117, 106898 (2023) |
| 31 | HARIS, A., ALEVRAS, P., MOHAMMADPOUR, M., THEODOSSIADES, S., and O' MAHONY, M. Design and validation of a nonlinear vibration absorber to attenuate torsional oscillations of propulsion systems. Nonlinear Dynamics, 100 (1), 33- 49 (2020) |
| 32 | WANG, F., ZHANG, J., XU, X., CAI, Y. F., ZHOU, Z. G., and SUN, X. Q. New teeth surface and back (TSB) modification method for transient torsional vibration suppression of planetary gear powertrain for an electric vehicle. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 140, 520- 537 (2019) |
| 33 | MAHÉV., , RENAULT, A., GROLET, A., MAHÉ, H., and THOMAS, O. The localised response and filtering performance of centrifugal pendulum vibration absorbers allowing a rotational mobility. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 571, 118028 (2024) |
| 34 | ZHANG, X., LIU, H., ZHAN, Z. B., WU, Y. H., ZHANG, W., TAHA, M., and YAN, P. F. Modelling and active damping of engine torque ripple in a power-split hybrid electric vehicle. Control Engineering Practice, 104, 104634 (2020) |
| 35 | GE, S. S., QIU, L. H., ZHANG, Z. G., WANG, H., and HU, M. H. Electromechanical coupling dynamic characteristics of electric drive system for electric vehicle. Nonlinear Dynamics, 112 (8), 6101- 6136 (2024) |
| 36 | ZHU, Z. Q., RUANGSINCHAIWANICH, S., and HOWE, D. Synthesis of cogging-torque waveform from analysis of a single stator slot. IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2 (3), 650- 657 (2006) |
| 37 | ZELLOUMA, D., BEKAKRA, Y., and BENBOUHENNI, H. Field-oriented control based on parallel proportional–integral controllers of induction motor drive. Energy Reports, 9, 4846- 4860 (2023) |
| 38 | AL-KAF, H. A. G., HAKAMI, S. S., and LEE, K. B. Hybrid current controller for permanent-magnet synchronous motors using robust switching techniques. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 38 (3), 3711- 3724 (2023) |
| 39 | YANG, D. C. H., and LIN, J. Y. Hertzian damping, tooth friction and bending elasticity in gear impact dynamics. Journal of Mechanical Design, 109, 189- 196 (1987) |
| 40 | LI, Z. X., and PENG, Z. Nonlinear dynamic response of a multi-degree of freedom gear system dynamic model coupled with tooth surface characters: a case study on coal cutters. Nonlinear Dynamics, 84 (1), 271- 286 (2015) |
| 41 | SONG, D. F., WU, J. J., YANG, D. P., CHEN, H. X., and ZENG, X. H. An adaptive torque ripple suppression algorithm for permanent magnet synchronous motor considering the influence of a transmission system. Journal of Vibration Engineering & Technologies, 10 (6), 2403- 2417 (2022) |
| 42 | GE, S. S., QIU, L. H., ZHANG, Z. G., GUO, D., and REN, H. H. Integrated impacts of non-ideal factors on the vibration characteristics of permanent magnet synchronous motors for electric vehicles. Machines, 10 (9), 739 (2022) |
| [1] | Hongyan CHEN, Youcheng ZENG, Hu DING, Siukai LAI, Liqun CHEN. Dynamics and vibration reduction performance of asymmetric tristable nonlinear energy sink [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(3): 389-406. |
| [2] | Jianing LIU, Jinqiang LI, Ying WU. Bandgap adjustment of a sandwich-like acoustic metamaterial plate with a frequency-displacement feedback control method [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(10): 1807-1820. |
| [3] | Jiawei MAO, Hao GAO, Junzhe ZHU, Penglin GAO, Yegao QU. Analytical modeling of piezoelectric meta-beams with unidirectional circuit for broadband vibration attenuation [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(10): 1665-1684. |
| [4] | Yong WANG, Peili WANG, Haodong MENG, Liqun CHEN. Dynamic performance and parameter optimization of a half-vehicle system coupled with an inerter-based X-structure nonlinear energy sink [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(1): 85-110. |
| [5] | Yuan YANG, Nenghui ZHANG, Hanlin LIU, Jiawei LING, Zouqing TAN. Piezoelectric and flexoelectric effects of DNA adsorbed films on microcantilevers [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2023, 44(9): 1547-1562. |
| [6] | Yang JIN, Tianzhi YANG. Enhanced vibration suppression and energy harvesting in fluid-conveying pipes [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2023, 44(9): 1487-1496. |
| [7] | Hu DING, J. C. JI. Vibration control of fluid-conveying pipes: a state-of-the-art review [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2023, 44(9): 1423-1456. |
| [8] | Youqi ZHANG, Rongyu XIA, Jie XU, Kefu HUANG, Zheng LI. Theoretical analysis of surface waves in piezoelectric medium with periodic shunting circuits [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2023, 44(8): 1287-1304. |
| [9] | Shengtao ZHANG, Jiaxi ZHOU, Hu DING, Kai WANG, Daolin XU. Fractional nonlinear energy sinks [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2023, 44(5): 711-726. |
| [10] | Weixing ZHANG, Wei ZHANG, Xiangying GUO. Vertical vibration control using nonlinear energy sink with inertial amplifier [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2023, 44(10): 1721-1738. |
| [11] | A. MOSLEMI, M. R. HOMAEINEZHAD. Effects of viscoelasticity on the stability and bifurcations of nonlinear energy sinks [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2023, 44(1): 141-158. |
| [12] | Hu DING, Yufei SHAO. NES cell [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2022, 43(12): 1793-1804. |
| [13] | Jian'en CHEN, Wei ZHANG, Jun LIU, Wenhua HU. Vibration absorption of parallel-coupled nonlinear energy sink under shock and harmonic excitations [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2021, 42(8): 1135-1154. |
| [14] | Jiren XUE, Yewei ZHANG, Hu DING, Liqun CHEN. Vibration reduction evaluation of a linear system with a nonlinear energy sink under a harmonic and random excitation [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2020, 41(1): 1-14. |
| [15] | Yimin WEI, Sha WEI, Qianlong ZHANG, Xinjian DONG, Zhike PENG, Wenming ZHANG. Targeted energy transfer of a parallel nonlinear energy sink [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2019, 40(5): 621-630. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||


 Email Alert
Email Alert RSS
RSS