Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (1): 1-24.doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-025-3204-7
Fan YANG1, Zhaoyang MA1,2, Xingming GUO1,2,†(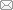 )
)
Received:2024-10-07
Revised:2024-11-27
Online:2025-01-03
Published:2025-01-06
Contact:
Xingming GUO
E-mail:xmguo@shu.edu.cn
Supported by:2010 MSC Number:
Fan YANG, Zhaoyang MA, Xingming GUO. Bandgap characteristics analysis and graded design of a novel metamaterial for flexural wave suppression. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2025, 46(1): 1-24.

Fig. 10
Band structures and vibration modes corresponding to the upper and lower boundaries of the bandgaps for the metamaterial with an elastic modulus of the substrate of (a) 7×107 Pa, (b) 2.1×108 Pa, and (c) 1×109 Pa or a mass density of the substrate of (d) 0.03×104 kg/m3, (e) 0.12×104 kg/m3, and (f) 0.63×104 kg/m3 (color online)"


Fig. 13
Band structure of (a) a short-substrate unit cell, (b) a long-substrate unit cell, (c) a uniform supercell, and (d) a dual-graded supercell, with the corresponding unit cell shown in each band structure. The graded green and orange colors in the dual-graded supercell represent the graded elastic modulus and mass, respectively (color online)"


Fig. 15
(a) Schematic diagram of a metamaterial formed by a periodic arrangement of 5 dual-graded supercells and (b) band structure of the dual-graded supercell and the frequency response function of the finite-length dual-graded metamaterial and metamaterial without resonators (color online)"


Fig. 17
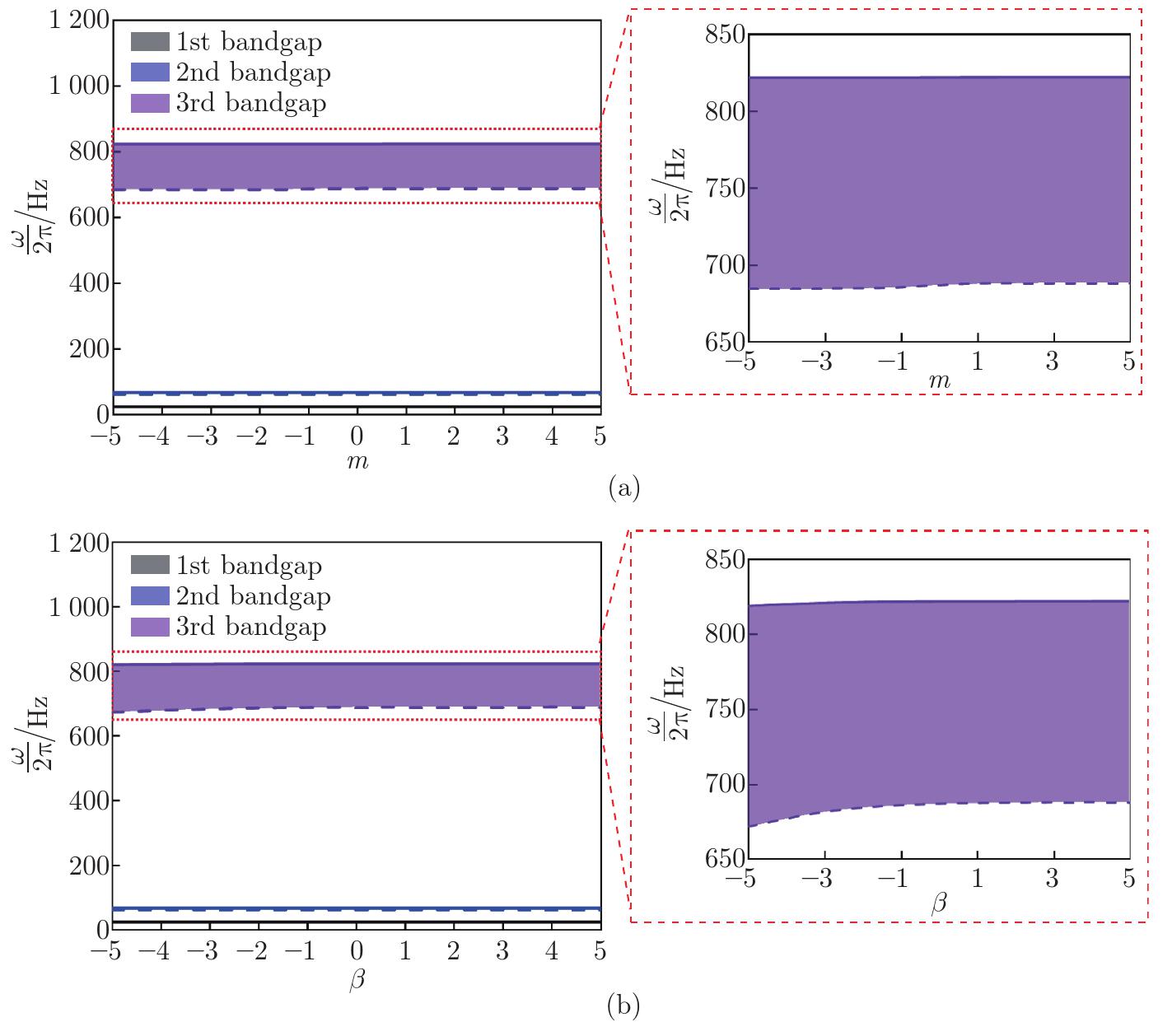
Bandgaps as a function of (a) the linear graded parameter m and (b) the inhomogeneous graded parameter β, where the elastic modulus of the elastic block is set to be 2.1×107 Pa, and other parameters are shown in Tables 1 and 2. The behavior of the 3rd bandgap is displayed in the enlarged view on the right (color online)"
| [1] | LEE, J. and KIM, Y. Y. Elastic metamaterials for guided waves: from fundamentals to applications. Smart Materials and Structures, 32(12), 123001 (2023) |
| [2] | MUHAMMAD and LIM, C. W. From photonic crystals to seismic metamaterials: a review via phononic crystals and acoustic metamaterials. Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering, 29(2), 1137–1198 (2022) |
| [3] | MA, F. Y., WANG, C., LIU, C. R., and WU, J. H. Structural designs, principles, and applications of thin-walled membrane and plate-type acoustic/elastic metamaterials. Journal of Applied Physics, 129(23), 231103 (2021) |
| [4] | KUSHWAHA, M. S., HALEVI, P., DOBRZYNSKI, L., and DJAFARI-ROUHANI, B. Acoustic band structure of periodic elastic composites. Physical Review Letters, 71(13), 2022–2025 (1993) |
| [5] | LIU, Z. Y., ZHANG, X. X., MAO, Y. W., ZHU, Y. Y., YANG, Z. Y., CHAN, C. T., and SHENG, P. Locally resonant sonic materials. Science, 289(5485), 1734–1736 (2000) |
| [6] | RUPIN, M., LEMOULT, F., LEROSEY, G., and ROUX, P. Experimental demonstration of ordered and disordered multiresonant metamaterials for Lamb waves. Physical Review Letters, 112(23), 234301 (2014) |
| [7] | LI, H. Z., LIU, X. C., LIU, Q., LI, S., YANG, J. S., TONG, L. L., SHI, S. B., SCHMIDT, R., and SCHROEDER, K. U. Sound insulation performance of double membrane-type acoustic metamaterials combined with a Helmholtz resonator. Applied Acoustics, 205, 109297 (2023) |
| [8] | LIN, Q. H., LIN, Q. L., WANG, Y. H., and DI, G. Q. Sound insulation performance of sandwich structure compounded with a resonant acoustic metamaterial. Composite Structures, 273, 114312 (2021) |
| [9] | XIAO, Z. Q., GAO, P. L., WANG, D. W., HE, X., and WU, L. Z. Ventilated metamaterials for broadband sound insulation and tunable transmission at low frequency. Extreme Mechanics Letters, 46, 101348 (2021) |
| [10] | SANGIULIANO, L., REFF, B., PALANDRI, J., WOLF-MONHEIM, F., PLUYMERS, B., DECKERS, E., DESMET, W., and CLAEYS, C. Low frequency tyre noise mitigation in a vehicle using metal 3D printed resonant metamaterials. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 179, 109335 (2022) |
| [11] | LI, Z. W., HU, H., and WANG, X. D. A new two-dimensional elastic metamaterial system with multiple local resonances. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 149, 273–284 (2018) |
| [12] | ZHOU, Y. C., YE, L., and CHEN, Y. Investigation of novel 3D-printed diatomic and local resonant metamaterials with impact mitigation capacity. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 206, 106632 (2021) |
| [13] | LIU, Z. Y., CHAN, C. T., and SHENG, P. Analytic model of phononic crystals with local resonances. Physical Review B, 71(1), 014103 (2005) |
| [14] | LIU, X. N., HU, G. K., HUANG, G. L., and SUN, C. T. An elastic metamaterial with simultaneously negative mass density and bulk modulus. Applied Physics Letters, 98(25), 251907 (2011) |
| [15] | LIU, Y. Q., SU, X. Y., and SUN, C. T. Broadband elastic metamaterial with single negativity by mimicking lattice systems. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 74, 158–174 (2015) |
| [16] | LU, L., RU, C. Q., and GUO, X. M. Vibration isolation of few-layer graphene sheets. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 185, 78–88 (2020) |
| [17] | LU, L., RU, C. Q., and GUO, X. M. Negative effective mass of a filled carbon nanotube. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 134, 174–181 (2017) |
| [18] | CHEN, J. S., SHARMA, B., and SUN, C. T. Dynamic behaviour of sandwich structure containing spring-mass resonators. Composite Structures, 93(8), 2120–2125 (2011) |
| [19] | NOUH, M., ALDRAIHEM, O., and BAZ, A. Vibration characteristics of metamaterial beams with periodic local resonances. Journal of Vibration and Acoustics-Transactions of the ASME, 136(6), 061012 (2014) |
| [20] | ZHU, R., LIU, X. N., HU, G. K., SUN, C. T., and HUANG, G. L. A chiral elastic metamaterial beam for broadband vibration suppression. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 333(10), 2759–2773 (2014) |
| [21] | YAN, Z. M., XIAO, H. J., LIU, Y. Y., and TAN, T. Band-gap dynamics and programming for low-frequency broadband elastic metamaterial. Composite Structures, 291, 115535 (2022) |
| [22] | CHEN, Y. M., FANG, X., WANG, J., FILIPPI, M., and CARRERA, E. An analysis of band gap characteristics of metamaterial plates with dual helix cells. Mechanics of Advanced Materials and Structures, 31(1), 92–102 (2024) |
| [23] | YANG, F., MA, Z. Y., and GUO, X. M. Bandgap characteristics of the two-dimensional missing rib lattice structure. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 43(11), 1631–1640 (2022) https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-022-2923-6 |
| [24] | ZHANG, Z. and HAN, X. K. A new hybrid phononic crystal in low frequencies. Physics Letters A, 380(45), 3766–3772 (2016) |
| [25] | AN, X. Y., LAI, C. L., HE, W. P., and FAN, H. L. Three-dimensional chiral meta-plate lattice structures for broad band vibration suppression and sound absorption. Composites Part B: Engineering, 224, 109232 (2021) |
| [26] | KHEYBARI, M., DARAIO, C., and BILAL, O. R. Tunable auxetic metamaterials for simultaneous attenuation of airborne sound and elastic vibrations in all directions. Applied Physics Letters, 121(8), 081702 (2022) |
| [27] | AN, X. Y., LAI, C. L., FAN, H. L., and ZHANG, C. Z. 3D acoustic metamaterial-based mechanical metalattice structures for low-frequency and broadband vibration attenuation. International Journal of Solids and Structures, 191, 293–306 (2020) |
| [28] | GERARD, N. J., OUDICH, M., XU, Z. P., YAO, D. S., CUI, H. C., NAIFY, C. J., IKEI, A., ROHDE, C. A., ZHENG, X. Y., and JING, Y. Three-dimensional trampolinelike behavior in an ultralight elastic metamaterial. Physical Review Applied, 16(2), 024015 (2021) |
| [29] | YAO, D. H., XIONG, M. K., LUO, J. Y., and YAO, L. Y. Flexural wave mitigation in metamaterial cylindrical curved shells with periodic graded arrays of multi-resonator. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 168, 108721 (2022) |
| [30] | ZHANG, L. W., BAI, Z. H., ZHANG, Q., JIN, Y., and CHEN, Y. F. On vibration isolation performance and crashworthiness of a three-dimensional lattice metamaterial. Engineering Structures, 292, 116510 (2023) |
| [31] | LU, X. C., WU, X. B., XIANG, H. R., SHEN, J., LI, Y. J., LI, Y. B., and WANG, X. S. Triple tunability of phononic bandgaps for three-dimensional printed hollow sphere lattice metamaterials. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 221, 107166 (2022) |
| [32] | ASSOUAR, M. B. and OUDICH, M. Enlargement of a locally resonant sonic band gap by using double-sides stubbed phononic plates. Applied Physics Letters, 100(12), 123506 (2012) |
| [33] | LI, S. B., CHEN, T. N., WANG, X. P., LI, Y. G., and CHEN, W. H. Expansion of lower-frequency locally resonant band gaps using a double-sided stubbed composite phononic crystals plate with composite stubs. Physics Letters A, 380(25-26), 2167–2172 (2016) |
| [34] | XIAO, Y., WEN, J. H., and WEN, X. S. Longitudinal wave band gaps in metamaterial-based elastic rods containing multi-degree-of-freedom resonators. New Journal of Physics, 14, 033042 (2012) |
| [35] | CHEN, H., LI, X. P., CHEN, Y. Y., and HUANG, G. L. Wave propagation and absorption of sandwich beams containing interior dissipative multi-resonators. Ultrasonics, 76, 99–108 (2017) |
| [36] | JIN, Y., JIA, X. Y., WU, Q. Q., HE, X., YU, G. C., WU, L. Z., and LUO, B. L. Design of vibration isolators by using the Bragg scattering and local resonance band gaps in a layered honeycomb meta-structure. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 521, 116721 (2022) |
| [37] | ZHANG, P. and TO, A. C. Broadband wave filtering of bioinspired hierarchical phononic crystal. Applied Physics Letters, 102(12), 121910 (2013) |
| [38] | HAO, S. T., SHENG, H., LIU, X. S., LI, H. Q., LI, S. H., and DING, Q. Low-frequency and broadband vibration absorption of a metamaterial plate with acoustic black hole resonators. Thin-Walled Structures, 202, 112073 (2024) |
| [39] | LI, X. P., CHEN, Y. Y., HU, G. K., and HUANG, G. L. A self-adaptive metamaterial beam with digitally controlled resonators for subwavelength broadband flexural wave attenuation. Smart Materials and Structures, 27(4), 045015 (2018) |
| [40] | LIN, L. F., LU, Z. Q., ZHAO, L., ZHENG, Y. S., DING, H., and CHEN, L. Q. Vibration isolation of mechatronic metamaterial beam with resonant piezoelectric shunting. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 254, 108448 (2023) |
| [41] | BELI, D., RUZZENE, M., and DE MARQUI, C. Bridging-coupling phenomenon in linear elastic metamaterials by exploiting locally resonant metachain isomers. Physical Review Applied, 14(3), 034032 (2020) |
| [42] | BANERJEE, A., DAS, R., and CALIUS, E. P. Frequency graded 1D metamaterials: a study on the attenuation bands. Journal of Applied Physics, 122(7), 075101 (2017) |
| [43] | LIU, C. C. and REINA, C. Broadband locally resonant metamaterials with graded hierarchical architecture. Journal of Applied Physics, 123(9), 095108 (2018) |
| [44] | WANG, Y. H., YANG, J., CHEN, Z. X., LIN, Y., GONG, L. P., ZHANG, S. W., LI, W. H., and SUN, S. S. Investigation of a magnetorheological elastomer metamaterial sandwich beam with tunable graded stiffness for broadband vibration attenuation. Smart Materials and Structures, 32(6), 065022 (2023) |
| [45] | AN, X. Y., YUAN, X. F., SUN, G. Q., HE, W. P., LAI, C. L., HOU, X. X., and FAN, H. L. Sandwich plate-type metastructures with periodic graded resonators for low-frequency and broadband vibration attenuation. Ocean Engineering, 298, 117229 (2024) |
| [46] | LI, X. F., CHENG, S. L., YANG, H. Y., YAN, Q., WANG, B., XIN, Y. J., SUN, Y. T., DING, Q., YAN, H., and LI, Y. J. Analysis of low frequency vibration attenuation and wave propagation mechanism of graded maze structure. Physica B: Condensed Matter, 649, 414519 (2023) |
| [47] | JIANG, W. F., YIN, M., LIAO, Q. H., XIE, L. F., and YIN, G. F. Three-dimensional single-phase elastic metamaterial for low-frequency and broadband vibration mitigation. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 190, 106023 (2021) |
| [48] | BANERJEE, A. Flexural waves in graded metabeam lattice. Physics Letters A, 388, 127057 (2021) |
| [49] | JIAN, Y. P., HU, G. B., TANG, L. H., TANG, W., ABDI, M., and AW, K. C. Analytical and experimental study of a metamaterial beam with grading piezoelectric transducers for vibration attenuation band widening. Engineering Structures, 275, 115091 (2023) |
| [50] | JIAN, Y. P., TANG, L. H., HU, G. B., LI, Z. Y., and AW, K. C. Design of graded piezoelectric metamaterial beam with spatial variation of electrodes. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 218, 107068 (2022) |
| [51] | SCHIMIDT, C. S., DE OLIVEIRA, L. P. R., and DE MARQUI, C. Vibro-acoustic performance of graded piezoelectric metamaterial plates. Composite Structures, 327, 117656 (2024) |
| [52] | YANG, N., LI, N. B., WANG, L., and LI, B. W. Thermal rectification and negative differential thermal resistance in lattices with mass gradient. Physical Review B, 76(2), 020301 (2007) |
| [53] | MELO, F., JOB, S., SANTIBANEZ, F., and TAPIA, F. Experimental evidence of shock mitigation in a Hertzian tapered chain. Physical Review E, 73(4), 041305 (2006) |
| [54] | HU, G. B., AUSTIN, A. C. M., SOROKIN, V., and TANG, L. H. Metamaterial beam with graded local resonators for broadband vibration suppression. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 146, 106982 (2021) |
| [55] | KRUSHYNSKA, A. O., KOUZNETSOVA, V. G., and GEERS, M. G. D. Visco-elastic effects on wave dispersion in three-phase acoustic metamaterials. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 96, 29–47 (2016) |
| [1] | Shuai MO, Xu TANG, Keren CHEN, H. HOUJOH, Wei ZHANG. Continuously adjustable mechanical metamaterial based on planetary gear trains and external meshing gears [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2025, 46(2): 233-. |
| [2] | Wei CHEN, Zhihong TANG, Yufen LIAO, Linxin PENG. A six-variable quasi-3D isogeometric approach for free vibration of functionally graded graphene origami-enabled auxeticmetamaterial plates submerged in a fluid medium [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2025, 46(1): 157-176. |
| [3] | Shuo WANG, Anshuai WANG, Yansen WU, Xiaofeng LI, Yongtao SUN, Zhaozhan ZHANG, Qian DING, G. D. AYALEW, Yunxiang MA, Qingyu LIN. Ultra-wide band gap and wave attenuation mechanism of a novel star-shaped chiral metamaterial [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(7): 1261-1278. |
| [4] | Long ZHAO, Zeqi LU, Hu DING, Liqun CHEN. A viscoelastic metamaterial beam for integrated vibration isolation and energy harvesting [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(7): 1243-1260. |
| [5] | Zhou HU, Zhibo WEI, Yan CHEN, Rui ZHU. Reconfigurable mechanism-based metamaterials for ternary-coded elastic wave polarizers and programmable refraction control [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(7): 1225-1242. |
| [6] | Xingzhong WANG, Shiteng RUI, Shaokun YANG, Weiquan ZHANG, Fuyin MA. A low-frequency pure metal metamaterial absorber with continuously tunable stiffness [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(7): 1209-1224. |
| [7] | Wei WEI, Feng GUAN, Xin FANG. A low-frequency and broadband wave-insulating vibration isolator based on plate-shaped metastructures [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(7): 1171-1188. |
| [8] | Changqi CAI, Chenjie ZHU, Fengyi ZHANG, Jiaojiao SUN, Kai WANG, Bo YAN, Jiaxi ZHOU. Modeling and analysis of gradient metamaterials for broad fusion bandgaps [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(7): 1155-1170. |
| [9] | Yuxin YAO, Yuansheng MA, Fang HONG, Kai ZHANG, Tingting WANG, Haijun PENG, Zichen DENG. On Klein tunneling of low-frequency elastic waves in hexagonal topological plates [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(7): 1139-1154. |
| [10] | Chao WANG, Honggang ZHAO, Yang WANG, Jie ZHONG, Dianlong YU, Jihong WEN. Topology optimization of chiral metamaterials with application to underwater sound insulation [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(7): 1119-1138. |
| [11] | Yabin JING, Lifeng WANG, Yuqiang GAO. Mass-spring model for elastic wave propagation in multilayered van der Waals metamaterials [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(7): 1107-1118. |
| [12] | M. SAFI, M. VAKILIFARD, M.J. MAHMOODI. Frequency-dependent viscoelasticity effects on the wave attenuation performance of multi-layered periodic foundations [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(3): 407-424. |
| [13] | Jianguo CUI, Tianzhi YANG, Wenju HAN, Liang LI, Muqing NIU, Liqun CHEN. Tunable topological interface states via a parametric system in composite lattices with/without symmetric elements [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(12): 2055-2074. |
| [14] | Yu ZHANG, Daming NIE, Xuyao MAO, Li LI. A thermodynamics-consistent spatiotemporally-nonlocal model for microstructure-dependent heat conduction [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(11): 1929-1948. |
| [15] | Jinhui LIU, Yu XUE, Zhihong GAO, A. O. KRUSHYNSKA, Jinqiang LI. Actively tunable sandwich acoustic metamaterials with magnetorheological elastomers [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(11): 1875-1894. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||


 Email Alert
Email Alert RSS
RSS