Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (1): 81-100.doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10483-025-3200-7
Previous Articles Next Articles
S. SAURABH, R. KIRAN†( ), D. SINGH, R. VAISH, V. S. CHAUHAN
), D. SINGH, R. VAISH, V. S. CHAUHAN
Received:2024-07-05
Revised:2024-11-22
Online:2025-01-03
Published:2025-01-06
Contact:
R. KIRAN
E-mail:raj@iitmandi.ac.in
2010 MSC Number:
S. SAURABH, R. KIRAN, D. SINGH, R. VAISH, V. S. CHAUHAN. A comprehensive investigation on nonlinear vibration andbending characteristics of bio-inspired helicoidallaminated composite structures. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2025, 46(1): 81-100.
Fig. 1
Numerous helicoidal structures observed at both macroscopic and microscopic levels in natural biology include (a) fingerprints and DNA extracted via the human body, (b) snail shells, (c) helicoidal fiber organization found in the dactyl club of the stomatopod ‘odontodactylus scyllarus’, (d) the exoskeleton of the beetle's elytron (green laminates), and (e) collagen fibril lamellae from the scales of ‘arapaima gigas’. (f) The helicoidal structure, inspired by the examples in (a)–(e), is utilized in designing (g) composite laminate layups. Potential fields where bio-inspired helicoidal composites can be applied include anti-low velocity impact solutions for (h) aircraft, (i) tanks, and (j) marines, as well as new energy applications including (k) wind turbine blades and (l) turbines[18] (color online)"
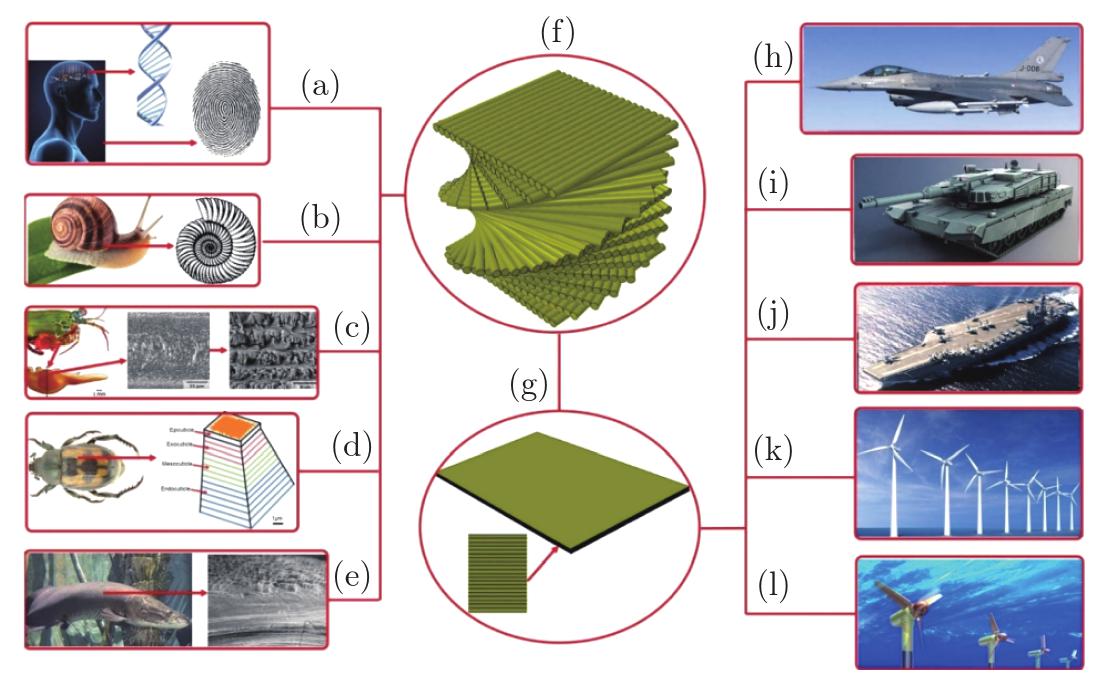
Table 1
The normalized natural frequencies ratio (ω¯nl/ω¯l) of 12-layered bio-inspired composite plate (E1/E2=10 and a/h=10) subject to the SSSS condition"
| Layup configuration | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 10 | HR1 | 1.044 7 | 1.181 5 | 1.382 4 | 1.428 3 | 1.535 5 |
| HR2 | 1.044 7 | 1.175 9 | 1.370 5 | 1.411 5 | 1.506 2 | ||
| HR3 | 1.044 7 | 1.171 7 | 1.360 8 | 1.401 7 | 1.493 2 | ||
| HE1 | 1.044 7 | 1.182 3 | 1.384 1 | 1.436 3 | 1.553 9 | ||
| HE2 | 1.044 7 | 1.178 1 | 1.375 5 | 1.430 4 | 1.537 2 | ||
| HE3 | 1.044 7 | 1.170 3 | 1.359 0 | 1.422 7 | 1.519 8 | ||
| HS1 | 1.044 7 | 1.143 5 | 1.302 5 | 1.498 9 | 1.450 5 | ||
| HS2 | 1.044 7 | 1.170 8 | 1.357 3 | 1.585 6 | 1.519 3 | ||
| HS3 | 1.044 7 | 1.167 5 | 1.351 3 | 1.577 3 | 1.589 1 | ||
| LH1 | 1.044 7 | 1.176 9 | 1.372 9 | 1.418 1 | 1.513 5 | ||
| LH2 | 1.044 7 | 1.173 7 | 1.366 1 | 1.411 0 | 1.501 0 | ||
| LH3 | 1.044 7 | 1.170 4 | 1.359 1 | 1.404 7 | 1.490 9 | ||
| FH | 1.044 4 | 1.169 3 | 1.355 8 | 1.401 2 | 1.490 8 | ||
| QI | 1.042 8 | 1.162 7 | 1.340 9 | 1.559 3 | 1.573 4 | ||
Table 2
The normalized natural frequencies ratio (ω¯nl/ω¯l) of 12-layered bio-inspired composite plate (E1/E2=10 and a/h=100) subject to the SSSS condition"
| Layup configuration | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 100 | HR1 | 1.030 8 | 1.140 5 | 1.298 6 | 1.497 5 | 1.483 2 |
| HR2 | 1.030 8 | 1.133 7 | 1.284 6 | 1.474 5 | 1.456 2 | ||
| HR3 | 1.030 8 | 1.127 4 | 1.271 5 | 1.452 8 | 1.436 0 | ||
| HE1 | 1.030 8 | 1.141 4 | 1.300 5 | 1.500 6 | 1.495 4 | ||
| HE2 | 1.030 8 | 1.136 8 | 1.291 1 | 1.485 4 | 1.488 0 | ||
| HE3 | 1.030 8 | 1.128 3 | 1.273 5 | 1.456 6 | 1.476 2 | ||
| HS1 | 1.030 8 | 1.100 3 | 1.215 0 | 1.360 7 | 1.529 3 | ||
| HS2 | 1.030 8 | 1.123 0 | 1.261 0 | 1.433 5 | 1.630 6 | ||
| HS3 | 1.030 8 | 1.123 8 | 1.263 0 | 1.437 3 | 1.636 8 | ||
| LH1 | 1.030 8 | 1.135 4 | 1.288 3 | 1.480 8 | 1.469 9 | ||
| LH2 | 1.030 8 | 1.131 8 | 1.280 8 | 1.468 6 | 1.459 4 | ||
| LH3 | 1.030 8 | 1.128 1 | 1.273 0 | 1.455 8 | 1.449 4 | ||
| FH | 1.032 4 | 1.124 8 | 1.265 9 | 1.443 8 | 1.435 1 | ||
| QI | 1.030 8 | 1.118 5 | 1.252 0 | 1.419 4 | 1.610 9 | ||
Table 3
The normalized natural frequencies ratio (ω¯nl/ω¯l) of 12-layered bio-inspired composite plate (E1/E2=40 and a/h=10) subject to the SSSS condition"
| Layup configuration | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40 | 10 | HR1 | 1.074 6 | 1.285 7 | 1.262 7 | 1.488 1 | 1.489 2 |
| HR2 | 1.072 7 | 1.276 6 | 1.261 8 | 1.518 5 | 1.529 3 | ||
| HR3 | 1.071 9 | 1.271 0 | 1.277 8 | 1.578 5 | 1.579 5 | ||
| HE1 | 1.074 5 | 1.285 9 | 1.273 5 | 1.482 4 | 1.501 6 | ||
| HE2 | 1.072 2 | 1.276 6 | 1.272 2 | 1.494 8 | 1.501 6 | ||
| HE3 | 1.068 0 | 1.259 1 | 1.281 5 | 1.544 5 | 1.501 6 | ||
| HS1 | 1.054 7 | 1.205 1 | 1.271 6 | 1.327 2 | 1.501 6 | ||
| HS2 | 1.068 5 | 1.255 3 | 1.352 2 | 1.399 1 | 1.501 6 | ||
| HS3 | 1.064 1 | 1.240 8 | 1.394 7 | 1.466 4 | 1.501 6 | ||
| LH1 | 1.072 3 | 1.276 3 | 1.254 4 | 1.496 7 | 1.501 6 | ||
| LH2 | 1.070 8 | 1.270 2 | 1.253 3 | 1.512 6 | 1.501 6 | ||
| LH3 | 1.069 4 | 1.263 9 | 1.254 5 | 1.349 4 | 1.501 6 | ||
| FH | 1.070 6 | 1.265 7 | 1.281 2 | 1.408 | 1.599 9 | ||
| QI | 1.062 4 | 1.233 2 | 1.479 3 | 1.453 | 1.501 6 | ||
Table 4
The normalized natural frequencies ratio (ω¯nl/ω¯l) of 12-layered bio-inspired composite plate (E1/E2=40 and a/h=100) subject to the SSSS condition"
| Layup configuration | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40 | 100 | HR1 | 1.041 5 | 1.162 1 | 1.198 2 | 1.257 1 | 1.450 0 |
| HR2 | 1.038 8 | 1.151 0 | 1.196 7 | 1.252 9 | 1.326 8 | ||
| HR3 | 1.036 4 | 1.141 2 | 1.201 9 | 1.260 2 | 1.334 6 | ||
| HE1 | 1.042 0 | 1.163 9 | 1.205 7 | 1.268 7 | 1.449 2 | ||
| HE2 | 1.040 3 | 1.156 8 | 1.215 9 | 1.278 1 | 1.366 1 | ||
| HE3 | 1.037 1 | 1.144 0 | 1.310 0 | 1.295 3 | 1.364 2 | ||
| HS1 | 1.027 0 | 1.104 5 | 1.223 9 | 1.375 3 | 1.349 6 | ||
| HS2 | 1.035 5 | 1.135 9 | 1.286 8 | 1.474 0 | 1.686 6 | ||
| HS3 | 1.035 7 | 1.136 7 | 1.289 0 | 1.478 6 | 1.694 7 | ||
| LH1 | 1.039 6 | 1.154 2 | 1.202 9 | 1.258 5 | 1.327 9 | ||
| LH2 | 1.038 1 | 1.148 4 | 1.204 8 | 1.258 3 | 1.322 3 | ||
| LH3 | 1.036 7 | 1.142 6 | 1.207 4 | 1.259 2 | 1.320 5 | ||
| FH | 1.035 5 | 1.137 6 | 1.208 8 | 1.268 6 | 1.344 1 | ||
| QI | 1.033 2 | 1.127 1 | 1.269 3 | 1.446 6 | 1.648 7 | ||
Table 5
The normalized natural frequencies ratio (ω¯nl/ω¯l) of 12-layered bio-inspired composite plate (E1/E2=10 and a/h=10) subject to the CCCC condition"
| Layup configuration | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 10 | HR1 | 1.018 2 | 1.071 5 | 1.156 7 | 1.269 9 | 1.260 5 |
| HR2 | 1.018 1 | 1.071 1 | 1.155 7 | 1.267 5 | 1.255 3 | ||
| HR3 | 1.018 2 | 1.071 5 | 1.156 2 | 1.267 6 | 1.257 5 | ||
| HE1 | 1.018 1 | 1.071 3 | 1.156 4 | 1.269 6 | 1.263 0 | ||
| HE2 | 1.017 9 | 1.070 5 | 1.154 5 | 1.266 1 | 1.261 2 | ||
| HE3 | 1.017 5 | 1.068 9 | 1.150 8 | 1.259 3 | 1.258 9 | ||
| HS1 | 1.015 9 | 1.062 3 | 1.136 1 | 1.232 9 | 1.248 1 | ||
| HS2 | 1.018 5 | 1.072 5 | 1.157 6 | 1.269 9 | 1.277 4 | ||
| HS3 | 1.017 2 | 1.067 5 | 1.147 3 | 1.252 2 | 1.377 7 | ||
| LH1 | 1.017 9 | 1.070 5 | 1.154 5 | 1.265 9 | 1.254 2 | ||
| LH2 | 1.017 8 | 1.070 0 | 1.153 2 | 1.263 5 | 1.251 5 | ||
| LH3 | 1.017 7 | 1.069 4 | 1.152 0 | 1.261 2 | 1.249 9 | ||
| FH | 1.018 1 | 1.070 9 | 1.154 8 | 1.265 1 | 1.257 4 | ||
| QI | 1.017 | 1.066 7 | 1.145 3 | 1.248 2 | 1.260 5 | ||
Table 6
The normalized natural frequencies ratio (ω¯nl/ω¯l) of 12-layered bio-inspired composite plate (E1/E2=10 and a/h=100) subject to the CCCC condition"
| Layup configuration | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 100 | HR1 | 1.010 2 | 1.040 4 | 1.089 3 | 1.155 1 | 1.235 9 |
| HR2 | 1.009 1 | 1.039 1 | 1.086 5 | 1.150 1 | 1.228 2 | ||
| HR3 | 1.009 6 | 1.038 0 | 1.083 8 | 1.145 5 | 1.220 9 | ||
| HE1 | 1.010 3 | 1.040 7 | 1.090 0 | 1.156 4 | 1.237 9 | ||
| HE2 | 1.010 2 | 1.040 2 | 1.088 9 | 1.154 4 | 1.234 7 | ||
| HE3 | 1.009 9 | 1.039 2 | 1.086 6 | 1.150 3 | 1.228 3 | ||
| HS1 | 1.008 7 | 1.034 5 | 1.076 1 | 1.131 9 | 1.200 0 | ||
| HS2 | 1.010 3 | 1.040 6 | 1.089 0 | 1.153 4 | 1.231 1 | ||
| HS3 | 1.010 1 | 1.039 9 | 1.087 7 | 1.151 3 | 1.228 5 | ||
| LH1 | 1.010 0 | 1.039 6 | 1.087 5 | 1.152 1 | 1.231 2 | ||
| LH2 | 1.009 9 | 1.039 0 | 1.086 2 | 1.149 6 | 1.227 4 | ||
| LH3 | 1.009 7 | 1.038 3 | 1.084 7 | 1.147 0 | 1.223 4 | ||
| FH | 1.009 5 | 1.037 6 | 1.083 1 | 1.144 2 | 1.219 0 | ||
| QI | 1.010 0 | 1.039 3 | 1.086 3 | 1.148 9 | 1.224 5 | ||
Table 7
The normalized natural frequencies ratio (ω¯nl/ω¯l) of 12-layered bio-inspired composite plate (E1/E2=40 and a/h=10) subject to the CCCC condition"
| Layup configuration | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40 | 10 | HR1 | 1.038 9 | 1.153 5 | 1.171 2 | 1.227 4 | 1.353 4 |
| HR2 | 1.039 5 | 1.154 9 | 1.176 | 1.237 1 | 1.398 7 | ||
| HR3 | 1.040 5 | 1.157 2 | 1.190 8 | 1.260 5 | 1.457 9 | ||
| HE1 | 1.038 3 | 1.151 3 | 1.171 8 | 1.201 1 | 1.345 4 | ||
| HE2 | 1.037 6 | 1.148 2 | 1.172 7 | 1.351 1 | 1.356 9 | ||
| HE3 | 1.036 0 | 1.141 5 | 1.177 7 | 1.245 1 | 1.390 7 | ||
| HS1 | 1.030 9 | 1.119 8 | 1.181 7 | 1.218 5 | 1.263 4 | ||
| HS2 | 1.037 4 | 1.144 8 | 1.209 3 | 1.238 0 | 1.267 2 | ||
| HS3 | 1.031 9 | 1.124 3 | 1.268 6 | 1.269 9 | 1.300 4 | ||
| LH1 | 1.038 5 | 1.151 5 | 1.167 7 | 1.214 3 | 1.376 9 | ||
| LH2 | 1.038 4 | 1.150 6 | 1.168 6 | 1.215 9 | 1.389 3 | ||
| LH3 | 1.038 2 | 1.149 6 | 1.712 0 | 1.219 8 | 1.412 4 | ||
| FH | 1.039 8 | 1.154 3 | 1.191 4 | 1.258 7 | 1.474 8 | ||
| QI | 1.032 1 | 1.124 2 | 1.266 4 | 1.261 6 | 1.294 5 | ||
Table 8
The normalized natural frequencies ratio (ω¯nl/ω¯l) of 12-layered bio-inspired composite plate (E1/E2=40 and a/h=100) subject to the CCCC condition"
| Layup configuration | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 40 | 100 | HR1 | 1.010 7 | 1.042 7 | 1.096 4 | 1.092 6 | 1.117 5 |
| HR2 | 1.010 2 | 1.040 8 | 1.091 7 | 1.091 4 | 1.114 3 | ||
| HR3 | 1.009 8 | 1.039 0 | 1.087 2 | 1.094 4 | 1.117 9 | ||
| HE1 | 1.010 8 | 1.043 2 | 1.097 6 | 1.095 8 | 1.122 9 | ||
| HE2 | 1.010 6 | 1.042 4 | 1.095 5 | 1.099 9 | 1.125 8 | ||
| HE3 | 1.010 2 | 1.040 8 | 1.091 3 | 1.111 0 | 1.135 7 | ||
| HS1 | 1.008 5 | 1.003 6 | 1.074 3 | 1.129 3 | 1.196 7 | ||
| HS2 | 1.010 8 | 1.042 5 | 1.093 2 | 1.160 2 | 1.241 1 | ||
| HS3 | 1.010 4 | 1.041 2 | 1.090 6 | 1.156 3 | 1.236 0 | ||
| LH1 | 1.010 4 | 1.041 6 | 1.093 5 | 1.093 9 | 1.117 0 | ||
| LH2 | 1.010 2 | 1.040 6 | 1.091 2 | 1.094 6 | 1.116 7 | ||
| LH3 | 1.009 9 | 1.039 6 | 1.088 8 | 1.096 0 | 1.117 3 | ||
| FH | 1.009 7 | 1.038 5 | 1.086 0 | 1.097 9 | 1.122 2 | ||
| QI | 1.010 3 | 1.040 5 | 1.088 9 | 1.153 2 | 1.230 8 | ||
| [1] | DOINEAU, E., CATHALA, B., BENEZET, J. C., BRAS, J., and LE MOIGNE, N. Development of bio-inspired hierarchical fibres to tailor the fibre/matrix interphase in (bio)composites. Polymers, 13(5), 804 (2021) |
| [2] | STUDART, A. R. Towards high-performance bioinspired composites. Advanced Materials, 24(37), 5024–5044 (2012) |
| [3] | HA, N. S. and LU, G. A review of recent research on bio-inspired structures and materials for energy absorption applications. Composites Part B: Engineering, 181, 107496 (2020) |
| [4] | WEGST, U. G. K., BAI, H., SAIZ, E., TOMSIA, A. P., and RITCHIE, R. O. Bioinspired structural materials. Nature Materials, 14(1), 23–36 (2014) |
| [5] | BAR-ON, B., BAYERLEIN, B., BLUMTRITT, H., and ZLOTNIKOV, I. Dynamic response of a single interface in a biocomposite structure. Physical Review Letters, 115(23), 238001 (2015) |
| [6] | CHEN, J., ZU, Q., WU, G., XIE, J., and TUO, W. Review of beetle forewing structures and their biomimetic applications in China: (II) on the three-dimensional structure, modeling and imitation. Materials Science and Engineering C: Materials for Biological Applications, 55, 620–633 (2015) |
| [7] | MOHAMED, S. A., MOHAMED, N., and ELTAHER, M. A. Bending, buckling and linear vibration of bio-inspired composite plates. Ocean Engineering, 259, 111851 (2022) |
| [8] | HEINEMANN, F., LAUNSPACH, M., GRIES, K., and FRITZ, M. Gastropod nacre: structure, properties and growth biological, chemical and physical basics. Biophysical Chemistry, 153(2-3), 126–153 (2011) |
| [9] | SUKSANGPANYA, N., YARAGHI, N. A., KISAILUS, D., and ZAVATTIERI, P. Twisting cracks in Bouligand structures. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 76, 38–57 (2017) |
| [10] | MENCATTELLI, L. and PINHO, S. T. Realising bio-inspired impact damage-tolerant thin-ply CFRP Bouligand structures via promoting diffused sub-critical helicoidal damage. Composites Science and Technology, 182 (2019) |
| [11] | MILLIRON, G. W., KISAILUS, D., WU, J., and GARAY, J. University of California Riverside Lightweight Impact-Resistant Composite Materials: Lessons from Mantis Shrimp, Ph.D. dissertation, University of Californic (2012) |
| [12] | TADAYON, M., AMINI, S., MASIC, A., and MISEREZ, A. The mantis shrimp saddle: a biological spring combining stiffness and flexibility. Advanced Functional Materials, 25(41), 6437–6447 (2015) |
| [13] | RAMAKRISHNA, D. and MURALI, G. B. Bio-inspired 3D-printed lattice structures for energy absorption applications: a review. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part L: Journal of Materials-Design and Applications, 237(3), 503–542 (2022) |
| [14] | GARULLI, T., KATAFIASZ, T. J., GREENHALGH, E. S., and PINHO, S. T. A novel bio-inspired microstructure for improved compressive performance of multidirectional CFRP laminates. Composites Part B: Engineering, 264, 110867 (2023) |
| [15] | CHOUHAN, G. and MURALI, G. B. Uniform and graded bio-inspired gyroid lattice: effects of post-curing and print orientation on mechanical property. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part L: Journal of Materials-Design and Applications, 238(5), 810–828 (2024) |
| [16] | GRUNENFELDER, L. K., SUKSANGPANYA, N., SALINAS, C., MILLIRON, G., YARAGHI, N., HERRERA, S., EVANS-LUTTEROOT, K., NUTT, S. R., ZAVATTIERI, P., and KISAILUS, D. Bio-inspired impact-resistant composites. Acta Biomater, 10(9), 3997–4008 (2014) |
| [17] | CHENG, L., THOMAS, A., GLANCEY, J. L., and KARLSSON, A. M. Mechanical behavior of bio-inspired laminated composites. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 42(2), 211–220 (2011) |
| [18] | JIANG, H., REN, Y., LIU, Z., ZHANG, S., and LIN, Z. Low-velocity impact resistance behaviors of bio-inspired helicoidal composite laminates with non-linear rotation angle-based layups. Composite Structures, 214, 463–475 (2019) |
| [19] | APICHATTRABRUT, T. and RAVI-CHANDAR, K. Helicoidal composites. Mechanics of Advanced Materials and Structures, 13(1), 61–76 (2006) |
| [20] | HAZZARD, M. K., HALLETT, S., CURTIS, P. T., IANNUCCI, L., and TRASK, R. S. Effect of fibre orientation on the low velocity impact response of thin Dyneema composite laminates. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 100, 35–45 (2017) |
| [21] | GINZBURG, D., PINTO, F., IERVOLINO, O., and MEO, M. Damage tolerance of bio-inspired helicoidal composites under low velocity impact. Composite Structures, 161, 187–203 (2017) |
| [22] | SHANG, J. S., NGERN, N. H. H., and TAN, V. B. C. Crustacean-inspired helicoidal laminates. Composites Science and Technology, 128, 222–232 (2016) |
| [23] | KARTHIKEYAN, K., KAZEMAHVAZI, S., and RUSSELL, B. P. Optimal fibre architecture of soft-matrix ballistic laminates. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 88, 227–237 (2016) |
| [24] | ASKARINEJAD, S. and RAHBAR, N. Mechanics of bioinspired lamellar structured ceramic/polymer composites: experiments and models. International Journal of Plasticity, 107, 122–149 (2018) |
| [25] | LIU, J. L., LEE, H. P., and TAN, V. B. C. Effects of inter-ply angles on the failure mechanisms in bioinspired helicoidal laminates. Composites Science and Technology, 165, 282–289 (2018) |
| [26] | ABIR, M. R., TAY, T. E., and LEE, H. P. On the improved ballistic performance of bio-inspired composites. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 123, 59–70 (2019) |
| [27] | BAHMANI, A., LI, G., WILLETT, T. L., and MONTESANO, J. Three-dimensional micromechanical assessment of bio-inspired composites with non-uniformly dispersed inclusions. Composite Structures, 212, 484–499 (2019) |
| [28] | YANG, F., XIE, W., and MENG, S. Global sensitivity analysis of low-velocity impact response of bio-inspired helicoidal laminates. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 187, 106110 (2020) |
| [29] | WANG, D., ZAHERI, A., RUSSELL, B., ESPINOSA, H., and ZAVATTIERI, P. Fiber reorientation in hybrid helicoidal composites. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 110, 103914 (2020) |
| [30] | LIU, J. L., SINGH, A. K., LEE, H. P., TAY, T. E., and TAN, V. B. C. The response of bio-inspired helicoidal laminates to small projectile impact. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 142, 103608 (2020) |
| [31] | CHEW, E., LIU, J. L., TAY, T. E., TRAN, L. Q. N., and TAN, V. B. C. Improving the mechanical properties of natural fibre reinforced laminates composites through biomimicry. Composite Structures, 258, 113208 (2021) |
| [32] | WANG, M., XU, Y. G., QIAO, P., and LI, Z. M. Buckling and free vibration analysis of shear deformable graphene-reinforced composite laminated plates. Composite Structures, 280, 114854 (2022) |
| [33] | LIU, J. L., MENCATTELLI, L., ZHI, J., CHUA, P. Y., TAY, T. E., and TAN, V. B. C. Lightweight, fiber-damage-resistant, and healable bio-inspired glass-fiber reinforced polymer laminate. Polymers, 14(3), 475 (2022) |
| [34] | SHARMA, A., BELARBI, M. O., GARG, A., and LI, L. Bending analysis of bio-inspired helicoidal/Bouligand laminated composite plates. Mechanics of Advanced Materials and Structures, 31, 5326–5340 (2023) |
| [35] | CHEN, J., ZHANG, X., OKABE, Y., SAITO, K., GUO, Z., and PAN, L. The deformation mode and strengthening mechanism of compression in the beetle elytron plate. Materials and Design, 131, 481–486 (2017) |
| [36] | ZHANG, X. M., XIE, J., CHEN, J. X., OKABE, Y., PAN, L. C., and XU, M. Y. The beetle elytron plate: a lightweight, high-strength and buffering functional-structural bionic material. Scientific Reports, 7, 4440 (2017) |
| [37] | WU, Y., LIU, Q., FU, J., LI, Q., and HUI, D. Dynamic crash responses of bio-inspired aluminum honeycomb sandwich structures with CFRP panels. Composites Part B: Engineering, 121, 122–133 (2017) |
| [38] | SUN, Z., LI, D., ZHANG, W., SHI, S., and GUO, X. Topological optimization of biomimetic sandwich structures with hybrid core and CFRP face sheets. Composites Science and Technology, 142, 79–90 (2017) |
| [39] | THAKUR, B. R., VERMA, S., SINGH, B. N., and MAITI, D. K. Dynamic analysis of folded laminated composite plate using nonpolynomial shear deformation theory. Aerospace Science and Technology, 106, 106083 (2020) |
| [40] | GUPTA, A. and GHOSH, A. Isogeometric static and dynamic analysis of laminated and sandwich composite plates using nonpolynomial shear deformation theory. Composites Part B: Engineering, 176, 107295 (2019) |
| [41] | SAYYAD, A. S. and GHUGAL, Y. M. On the free vibration analysis of laminated composite and sandwich plates: a review of recent literature with some numerical results. Composite Structures, 129, 177–201 (2015) |
| [42] | ABRATE, S. and DI SCIUVA M. Equivalent single layer theories for composite and sandwich structures: a review. Composite Structures, 179, 482–494 (2017) |
| [43] | VERMA, S., THAKUR, B. R., SINGH, B. N., and MAITI, D. K. Geometrically nonlinear flexural analysis of multilayered composite plate using polynomial and non-polynomial shear deformation theories. Aerospace Science and Technology, 112, 106635 (2021) |
| [44] | GROVER, N., MAITI, D. K., and SINGH, B. N. A new inverse hyperbolic shear deformation theory for static and buckling analysis of laminated composite and sandwich plates. Composite Structures, 95, 667–675 (2013) |
| [45] | SINGH, D., KIRAN, R., and VAISH, R. Vibration and buckling analysis of agglomerated CNT composite plates via isogeometric analysis using non-polynomial shear deformation theory. European Journal of Mechanics-A/Solids, 98, 104892 (2023) |
| [46] | SHUFRIN, I., RABINOVITCH, O., and EISENBERGER, M. A semi-analytical approach for the geometrically nonlinear analysis of trapezoidal plates. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 52(12), 1588–1596 (2010) |
| [47] | DASH, P. and SINGH, B. N. Static response of geometrically nonlinear laminated composite plates having uncertain material properties. Mechanics of Advanced Materials and Structures, 22(4), 269–280 (2015) |
| [48] | TRAN, L. V., LEE, J., NGUYEN-VAN, H., NGUYEN-XUAN, H., and WAHAB, M. A. Geometrically nonlinear isogeometric analysis of laminated composite plates based on higher-order shear deformation theory. International Journal of Non-linear Mechanics, 72, 42–52 (2015) |
| [49] | PHUNG-VAN, P., NGUYEN-THOI, T., BUI-XUAN, T., and LIEU-XUAN, Q. A cell-based smoothed three-node Mindlin plate element (CS-FEM-MIN3) based on the C0-type higher-order shear deformation for geometrically nonlinear analysis of laminated composite plates. Computational Materials Science, 96(PB), 549–558 (2015) |
| [50] | ANSARI, R., HASSANI, R., GHOLAMI, R., and ROUHI, H. Nonlinear bending analysis of arbitrary-shaped porous nanocomposite plates using a novel numerical approach. International Journal of Non-linear Mechanics, 126, 103556 (2020) |
| [51] | BENNACEUR, M. A. and XU, Y. Application of the natural element method for the analysis of composite laminated plates. Aerospace Science and Technology, 87, 244–253 (2019) |
| [52] | SINGH, G., and RAO, Y. V. K. S. Large deflection behaviour of thick composite plates. Composite Structures, 8(1), 13–29 (1987) |
| [53] | REDDY, J. N. Mechanics of Laminated Composite Plates and Shells: Theory and Analysis, CRC Press, Florida (2004) |
| [54] | LE-MANH, T., LUU-ANH, T., and LEE, J. Isogeometric analysis for flexural behavior of composite plates considering large deformation with small rotations. Mechanics of Advanced Materials and Structures, 23(3), 328–336 (2016) |
| [55] | DASH, P. and SINGH, B. N. Geometrically nonlinear bending analysis of laminated composite plate. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 15(10), 3170–3181 (2010) |
| [1] | Xuefeng WANG, Zhan SHI, Qiqi YANG, Yuzhi CHEN, Xueyong WEI, Ronghua HUAN. Recent advancements of nonlinear dynamics in mode coupled microresonators: a review [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2025, 46(2): 209-. |
| [2] | Jie CHEN, Xinyue ZHANG, Mingyang FAN. Dynamic behaviors of graphene platelets-reinforced metal foam piezoelectric beams with velocity feedback control [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2025, 46(1): 63-80. |
| [3] | Xinyu LIAN, Bing LIU, Huaxia DENG, Xinglong GONG. A vibration isolator with a controllable quasi-zero stiffness region based on nonlinear force design [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(8): 1279-1294. |
| [4] | Jiamei WANG, Siukai LAI, Chen WANG, Yiting ZHANG, Zhaolin CHEN. On the role of sliding friction effect in nonlinear tri-hybrid vibration-based energy harvesting [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(8): 1295-1314. |
| [5] | Lele REN, Wei ZHANG, Yufei ZHANG. Inter-well internal resonance analysis of rectangular asymmetric cross-ply bistable composite laminated cantilever shell under transverse foundation excitation [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(8): 1353-1370. |
| [6] | Zeyu CHAI, J. T. HAN, Xuyuan SONG, Jian ZANG, Yewei ZHANG, Zhen ZHANG. Theoretical and experimental investigations on an X-shaped vibration isolator with active controlled variable stiffness [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(8): 1371-1386. |
| [7] | Long ZHAO, Zeqi LU, Hu DING, Liqun CHEN. A viscoelastic metamaterial beam for integrated vibration isolation and energy harvesting [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(7): 1243-1260. |
| [8] | Meng LI, Hu DING. A vertical track nonlinear energy sink [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(6): 931-946. |
| [9] | Lele REN, Wei ZHANG, Ting DONG, Yufei ZHANG. Snap-through behaviors and nonlinear vibrations of a bistable composite laminated cantilever shell: an experimental and numerical study [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(5): 779-794. |
| [10] | Yiming CAO, Hui MA, Xumin GUO, Bingfeng ZHAO, Hui LI, Xin WANG, Bing WANG. Comparison of nonlinear modeling methods for the composite rubber clamp [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(5): 763-778. |
| [11] | E. GHAVANLOO, S. EL-BORGI. Nonlinear wave dispersion in monoatomic chains with lumped and distributed masses: discrete and continuum models [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(4): 633-648. |
| [12] | Hongyan CHEN, Youcheng ZENG, Hu DING, Siukai LAI, Liqun CHEN. Dynamics and vibration reduction performance of asymmetric tristable nonlinear energy sink [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(3): 389-406. |
| [13] | M. ABBASI GAVARI, M. R. HOMAEINEZHAD. Nonlinear dynamic modeling of planar moving Timoshenko beam considering non-rigid non-elastic axial effects [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(3): 479-496. |
| [14] | Runqing CAO, Zilong GUO, Wei CHEN, Huliang DAI, Lin WANG. Nonlinear dynamics of a circular curved cantilevered pipe conveying pulsating fluid based on the geometrically exact model [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(2): 261-276. |
| [15] | Zhanhuan YAO, Tieding GUO, Wanzhi QIAO. Modeling and analysis of an inextensible beam with inertial and geometric nonlinearities [J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics (English Edition), 2024, 45(12): 2113-2130. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||


 Email Alert
Email Alert RSS
RSS